
Are you looking for low-cost options to help the family stay cool this summer? The Gold Coast is home to a host of free or low-cost, family-friendly swimming spots that are sure to cool everyone off and provide hours of fun entertainment. Here are 8 spots to try this summer, from the northern most parts of the Gold Coast, right down to the southern Gold Coast.
Lions Park is located at the Jacobs Well Boat Ramp, and is a council-managed, netted swimming enclosure nearby the mouth of the Pimpama River. Here you will find a small sandy beach area with shade sails right up to the water’s edge, as well as barbeque and picnic facilities. This spot is great for younger children, as they can get a taste of the beach without large waves or long walks from the car to the water. Best visited at high tide, it can be a bit muddy at low tide.

Cabbage Tree Point is a small town just near Jacobs Well, with a boat ramp, small beach and Charlie Hammel Park. This is a great spot for the family to spend a morning – set up a picnic blanket under the trees by the ship-themed playground and enjoy a swim at the small, sandy beach. Again, being on the river this is best visited at high tide, but enjoyable all day long.
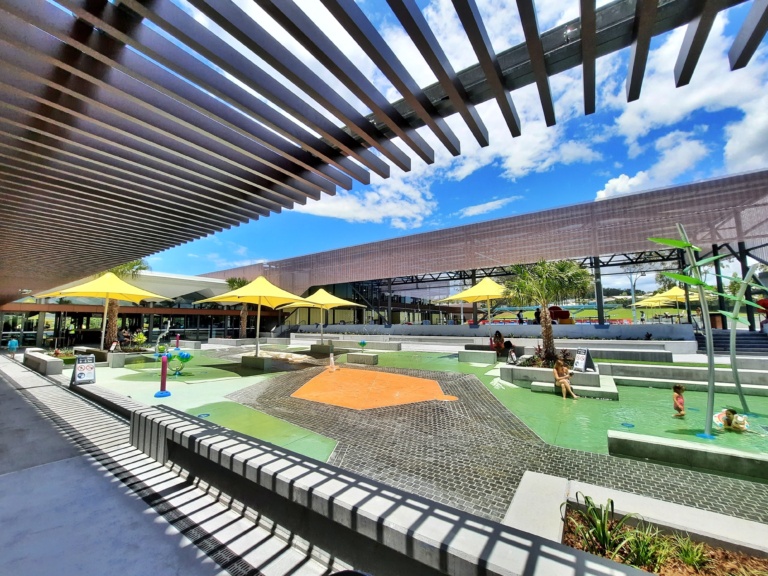

The Pimpama Sports Hub is the northern Gold Coast’s largest aquatic centre, with a 50-metre outdoor swimming pool, a 25-metre indoor swimming pool, learn to swim pool and a hydrotherapy pool. The children’s splash pad is exceptional, with water fountains, bubbling brooks and water at ankle depth – it’s ideal for toddler and primary school aged children.
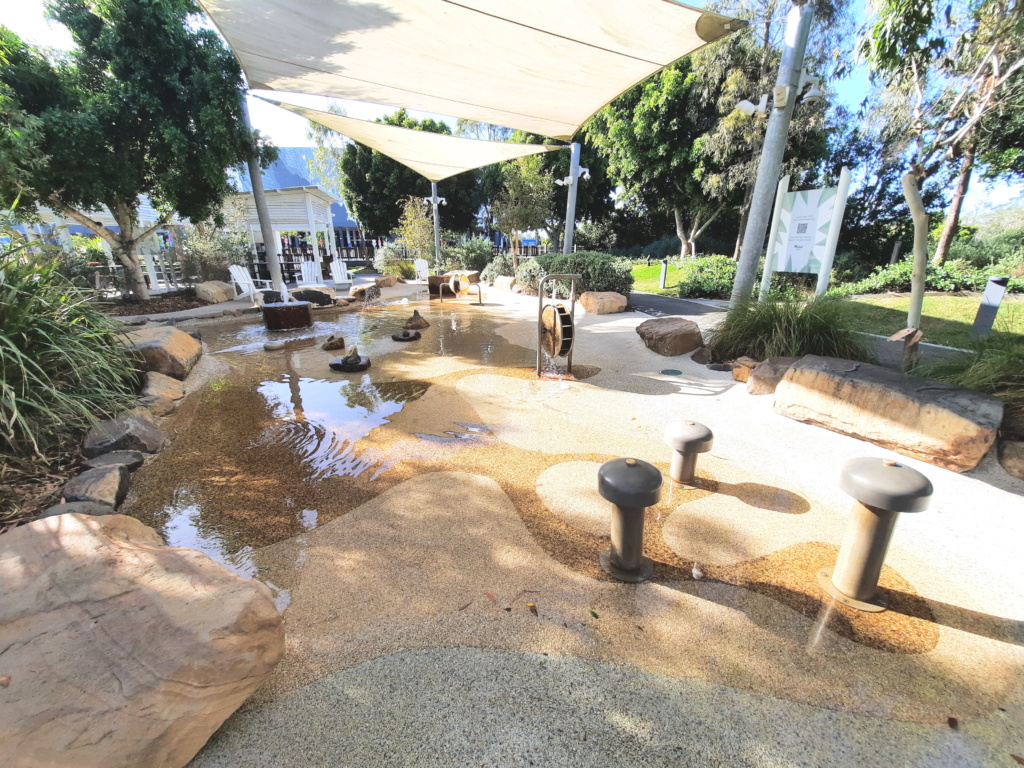

A splash pad might be the last thing you would expect to find at a shopping centre, but Westfield Coomera has one of the best free waterplay areas on the Gold Coast. Designed to resemble a billabong, waterways weave around interactive play stations where children can play with squirting frogs and jump across stepping stones. There are excellent change room facilities available and a café next door.
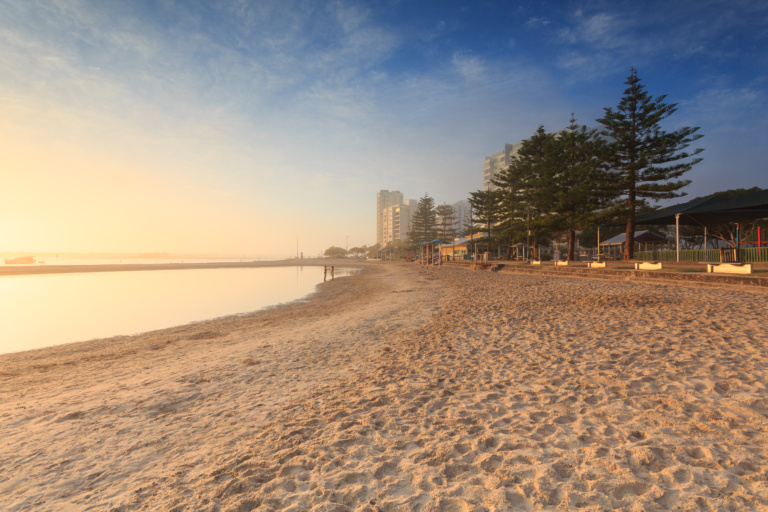

Ian Dipple Lagoon is a great place to go for a swim. Protected by a large sandbank, this lagoon is wave free and perfect for little ones. There are shower and toilet facilities along the shore as well, making the pack up easy. In the evenings, the lagoon is floodlit, so it’s also a great spot for dinner time fish and chips.
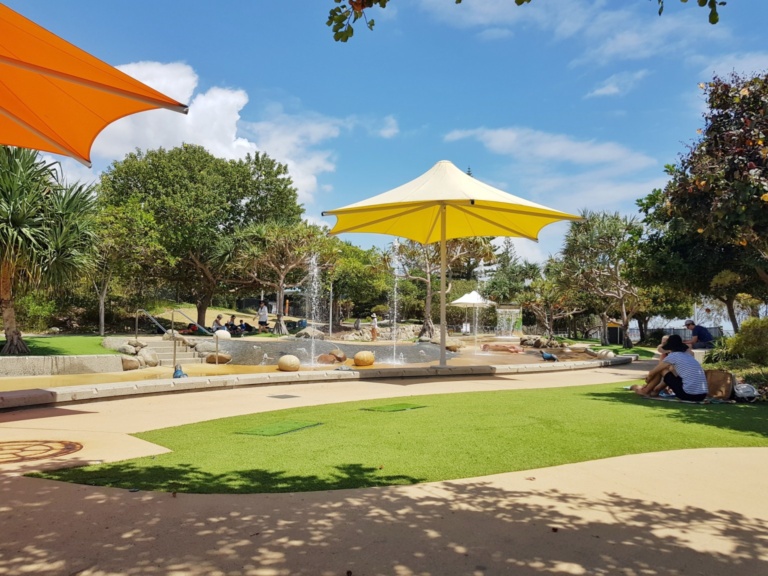

The Broadwater Rockpools might be the most popular water play space on the Gold Coast, with plenty of water fountains and vibrant marine-themed equipment to play with. The water play is built to resemble a creek bed, and it works like tidal rockpools with the water receding every 5-10 minutes and then returning again. The Rockpools are watched over by lifeguards during opening hours and it’s completely free to play.
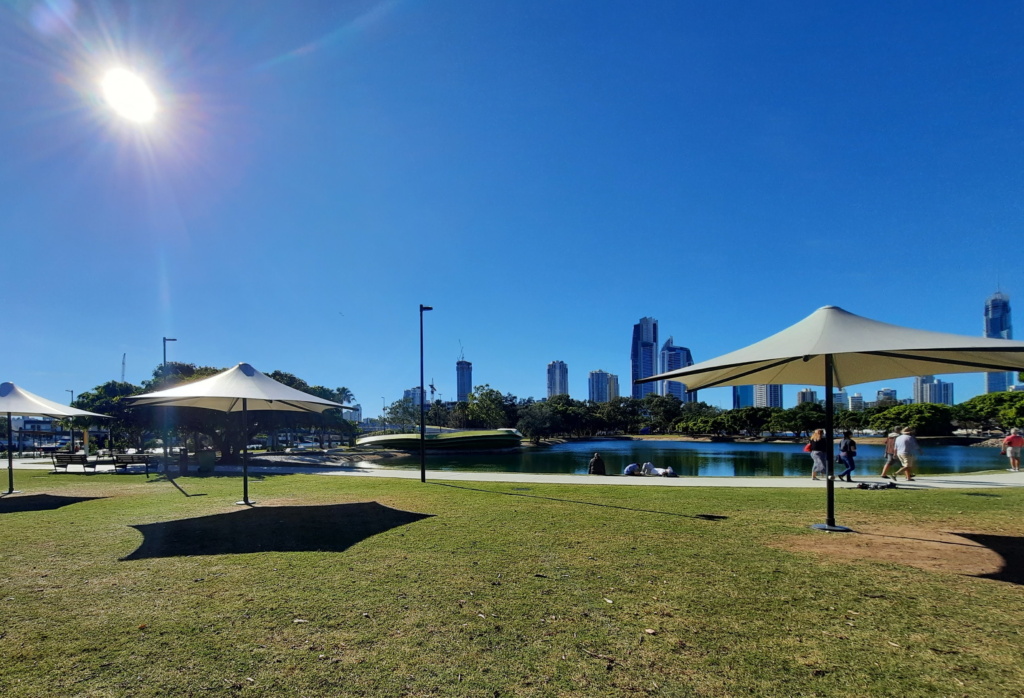

Located within the Home of the Arts precinct, Evandale Lake is a popular swimming spot for Gold Coasters. With a sandy beach around the outside, the lake has shallow edges but can be deceptively deep as you get further in. Families love to spend the day here, making the most of weekend food markets or a picnic lunch. There is a fun shaded playground by the lagoon too.
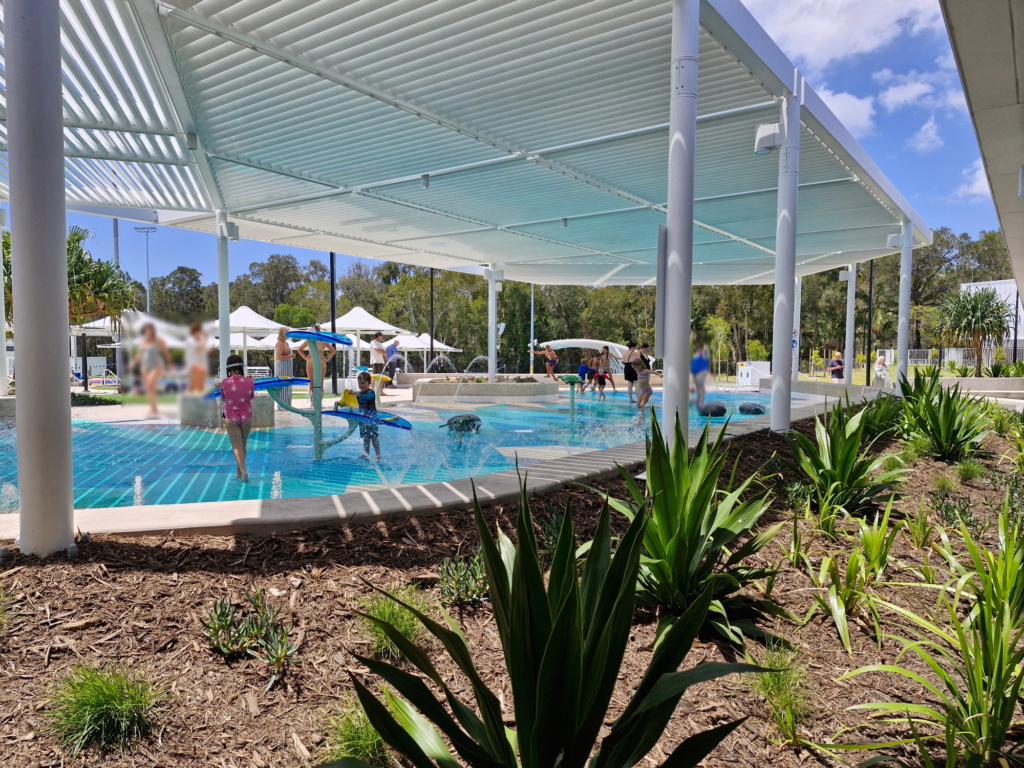

The newest water play destination on the Gold Coast, the Palm Beach Aquatic Centre opened at the end of October and now has a 50m outdoor pool, 25m outdoor pool, indoor warm water program pool, 25m indoor learn to swim pool, and an outdoor splash pad. The splash pad at Palm Beach is fairly simple in design, with plenty of sprayers along the ground as well as a few water play towers and spinners, but it is made entirely of a rubber base which is absolutely ideal for those crawling or learning to walk!
If you’re looking for early education and care for your young family, look no further than Little Scholars!
We offer your child the very best facilities, resources and early educational, play-based programs available, which are underpinned by the early years learning framework. We also believe in fun, wide-ranging experiences so that children can begin to develop interests and passions of their own, from Bush Kinder adventures to our broad extracurricular program which includes swimming for our kindergarten children, we believe in keeping wonder and magic in childhood.
Find Lara’s recommendations at her website Mrs. Lardeedah.com, and follow her socials Facebook and Instagram

Grandparents have always shared a special bond with their grandchildren, but nowadays they are also playing an increasingly important role as a caregiver, as children spend much more time with their grandparents than ever before. Sometimes however, the generation gap can make it hard to think of new and fun things to do together that appeal to everyone.
Whether the grandchildren are spending an afternoon, a weekend, or the school holidays with you, this list is sure to keep children and grandparents of all interests and physical abilities, entertained and making memories year-round.

Each year, World Science Festival Brisbane paints the town red and takes science out of the laboratory and into the streets, parks, museums, galleries and performing arts venues of Brisbane and regional Queensland! World Science Festival Brisbane offers interactive and informative experiences for inquisitive young minds, with a huge range of family-friendly events and workshops.
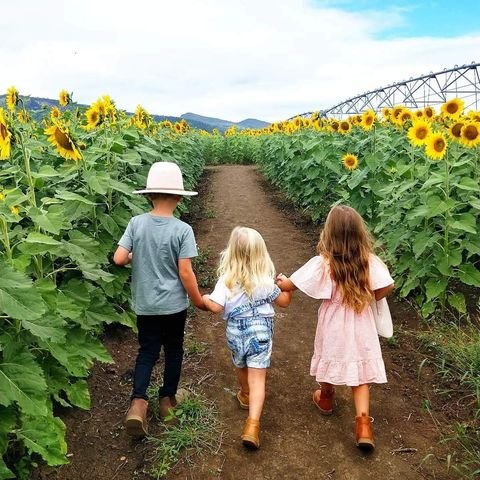

Gather your family and friends and join in a fun weekend in the Scenic Rim region, filled with live entertainment, workshops for children, cooking classes, mini photo sessions, arts, crafts and much more. Don’t forget the star of the show – strolling through beautiful sunflower fields and picking your own to take home.
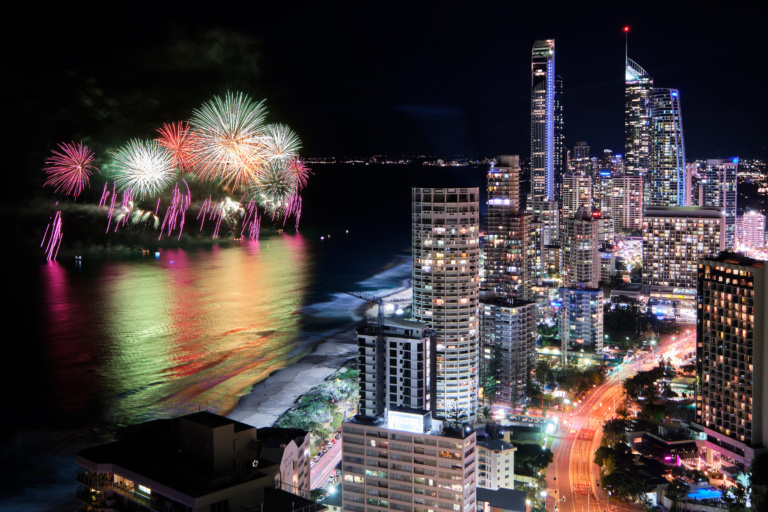

Surfers Paradise beach becomes a playground of light, music and entertainment at SeaFire, Australia’s only international fireworks competition. Nations compete to take home the SeaFire Championship title, so this is a chance to see choreographed fireworks displays fired off ocean barges. Bring your picnic blanket and set up in the sand for beautiful firework vistas. There is also plenty of pre-entertainment including food trucks, music and roving performances.
5-8 pm, free!
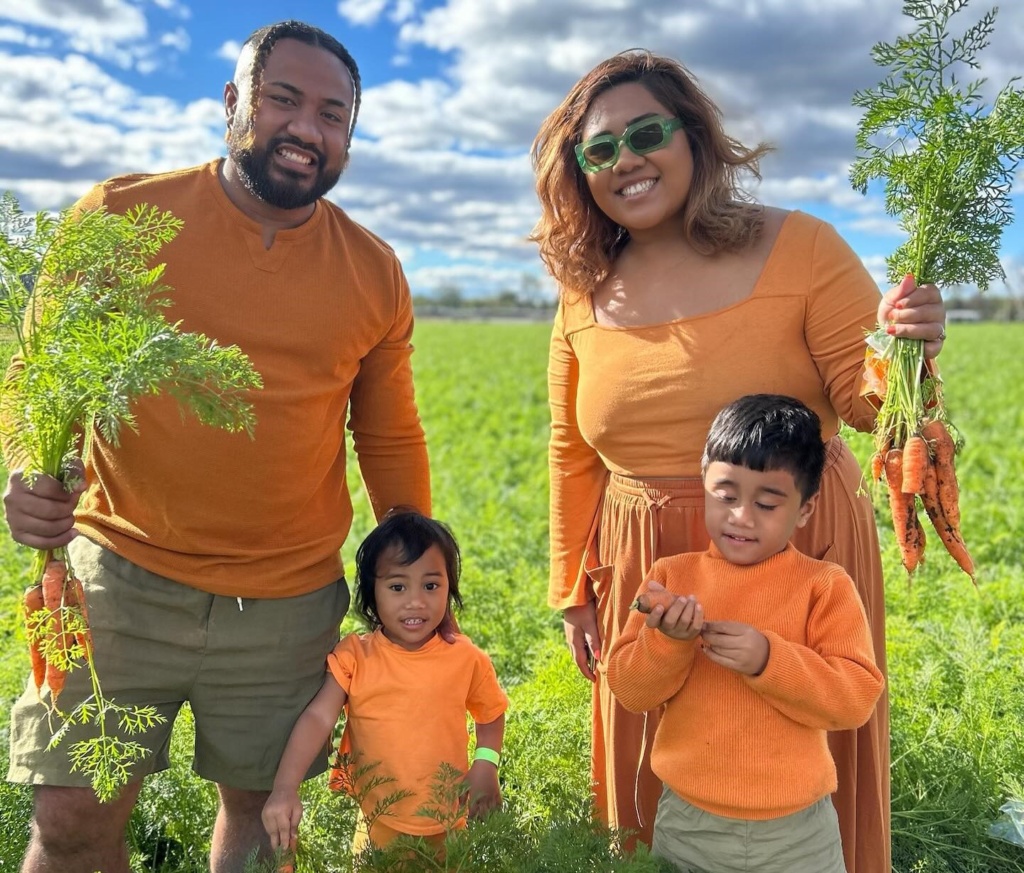

Kalfresh Vegetables throw open the doors to their farm and factory and welcome carrot-loving visitors each June!
See how they grow, pick, wash and pack carrots, as well as celebrate all things carrot with carrot juice, carrot sausages, carrot cake and carrot bread! Everyone can get their hands dirty with carrot picking on the farm, taking home as many as you can carry.
This year’s date has yet to be released, so keep an eye on Kalfresh’s social media channels for its official date. This is held on the Scenic Rim, at Kalbar on the Cunningham Highway in the Fassifern Valley.
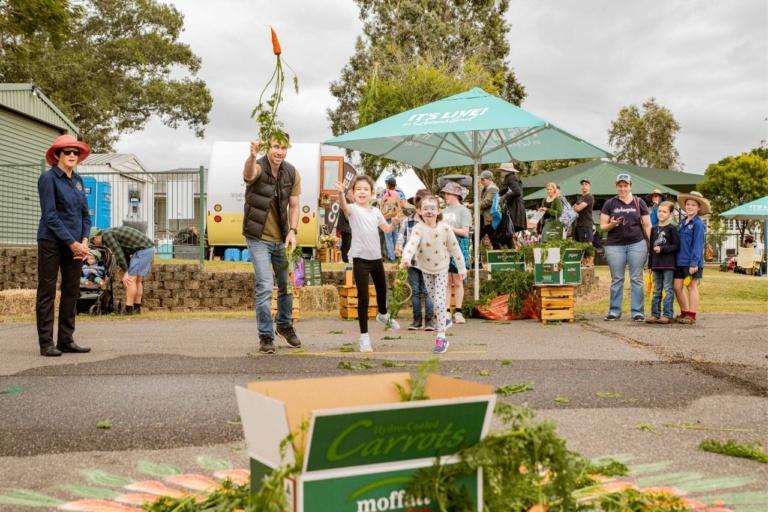

The Winter Harvest Festival is the Scenic Rim’s signature event where you can experience Eat Local Month in one glorious, flavour-filled day! Chefs, growers. producers, and artisans come together to showcase the region’s culinary treasures. There will be more than 60 market stalls offering fresh seasonal produce, local wines, beers and spirits, cheeses, meats, and more. Alongside these culinary delights, you’ll find a variety of handcrafted goods and local creations, all crafted by the region’s skilled artisans.
There are food displays, workshops, produce stalls and a huge festival environment where the children can take part in a variety of games, activities and food related fun.nteractive activities like tractor pulling, carrot tossing, and farm animal cuddles. They’ll enjoy face painting, garden games, and fun, educational experiences that teach them about agriculture and food in a hands-on way.
Don’t miss the annual Tractor Pull competition!
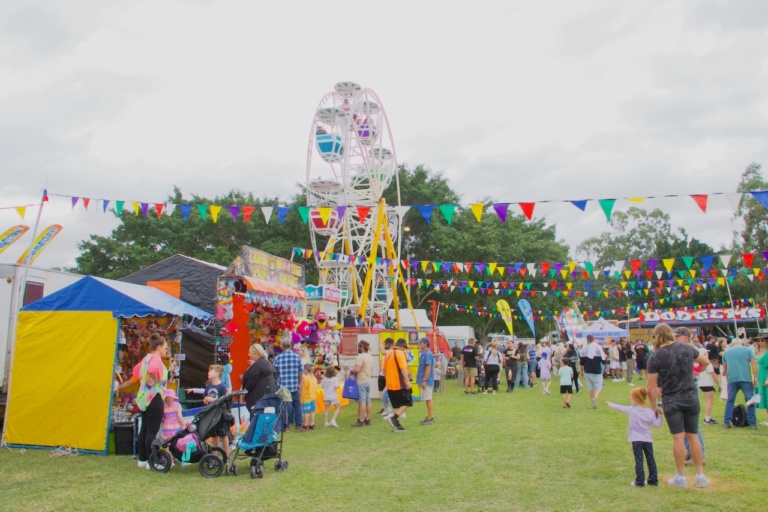

Where country meets the Gold Coast! Get up close and personal with cute animals, meet the farmers and exhibitors and taste delicious foods made from locally sourced ingredients. Watch the woodchop, and enjoy the equestrian program. Wander through the pavilions, check out the crafts and cooking, from honey to homebrew, lace to LEGO, fine arts to photography, and flowers to fruit sculptures and explore the best agriculture has to offer. Finish the day off with an incredible fireworks display!
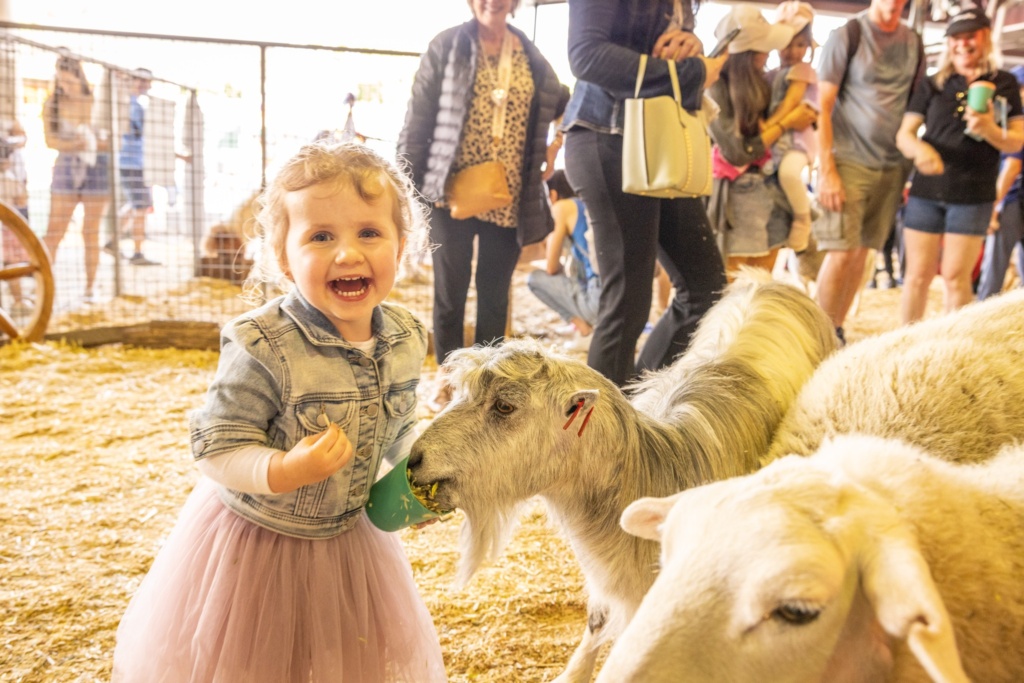

The Royal Queensland Show (Ekka) is Queensland’s largest and most loved annual event, now in its 149th year, bringing the country and the city together for a big celebration of agriculture. Enjoy competition entries from woodchop to giant vegetables, there’s 10,000 animals from beef cattle to cats and dogs, world-class live entertainment, award-winning food and wine, carnival rides and showbags, family shopping, educational activities and much more.

The Pacific Airshow Gold Coast is a three-day weekend event that features aerobatic demonstrations by the world’s best aviators. Attendees can join in meet and greets with the pilots, check out the family zone packed with aviation themed games and activities, and relax beachfront while watching paratroopers, stunt planes, helicopters, military planes and more from around the world perform.
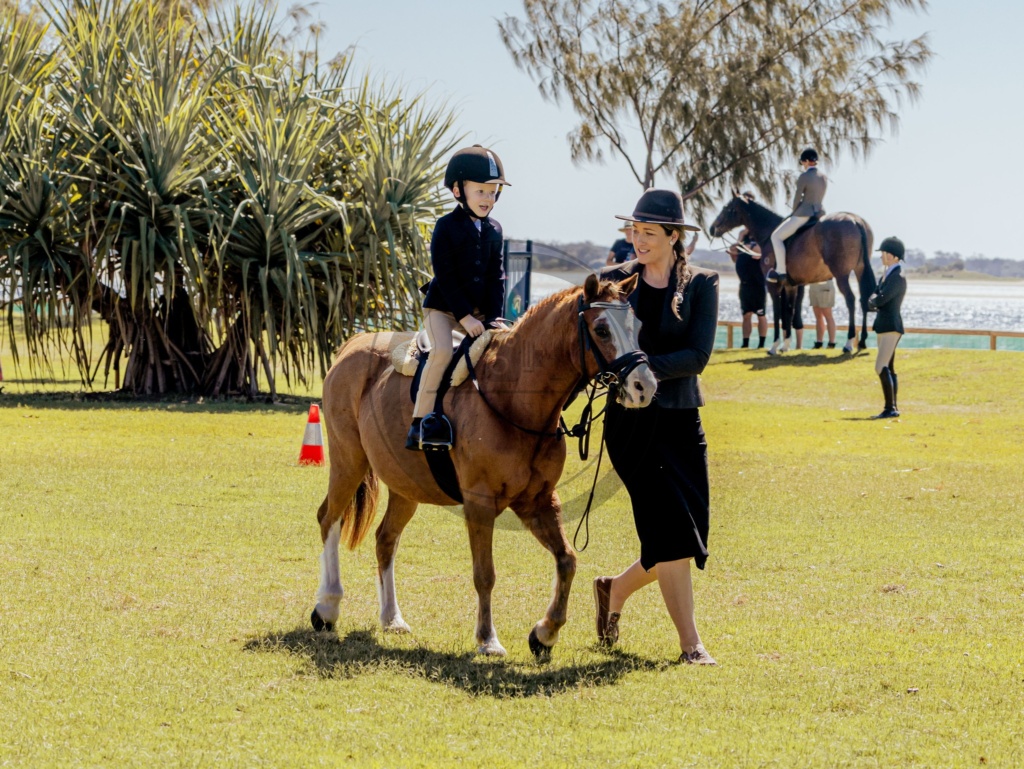

Immerse yourself in the family fun and excitement of the Gold Coast Show! Set on the beautiful Broadwater Parklands on the Gold Coast, this FREE show attracts tens of thousands of families annually. Enjoy woodchop, equestrian, food and beverage stalls, exhibits, games and rides. Each night also concludes with an incredible fireworks show.
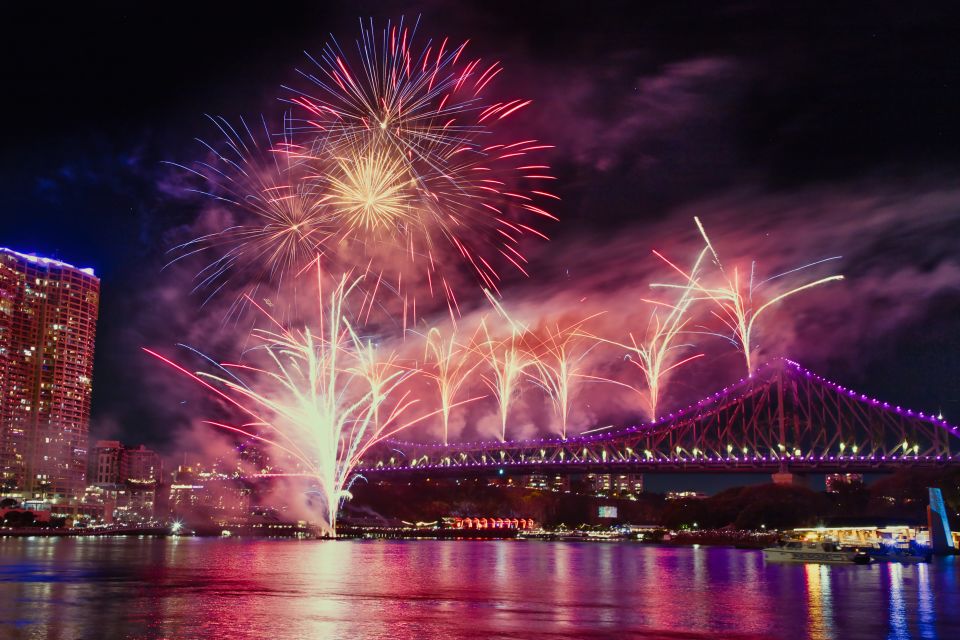

Riverfire is Brisbane’s most spectacular night of the year. The launch event for the three-week Brisbane Festival, Riverfire brings families from across south-east Queensland to South Bank for a night that lights up the skies. Entertainment begins from 4pm, including an RAAF aerial display, with the main event – the state’s most spectacular annual fireworks display – lighting up the sky at 7pm.
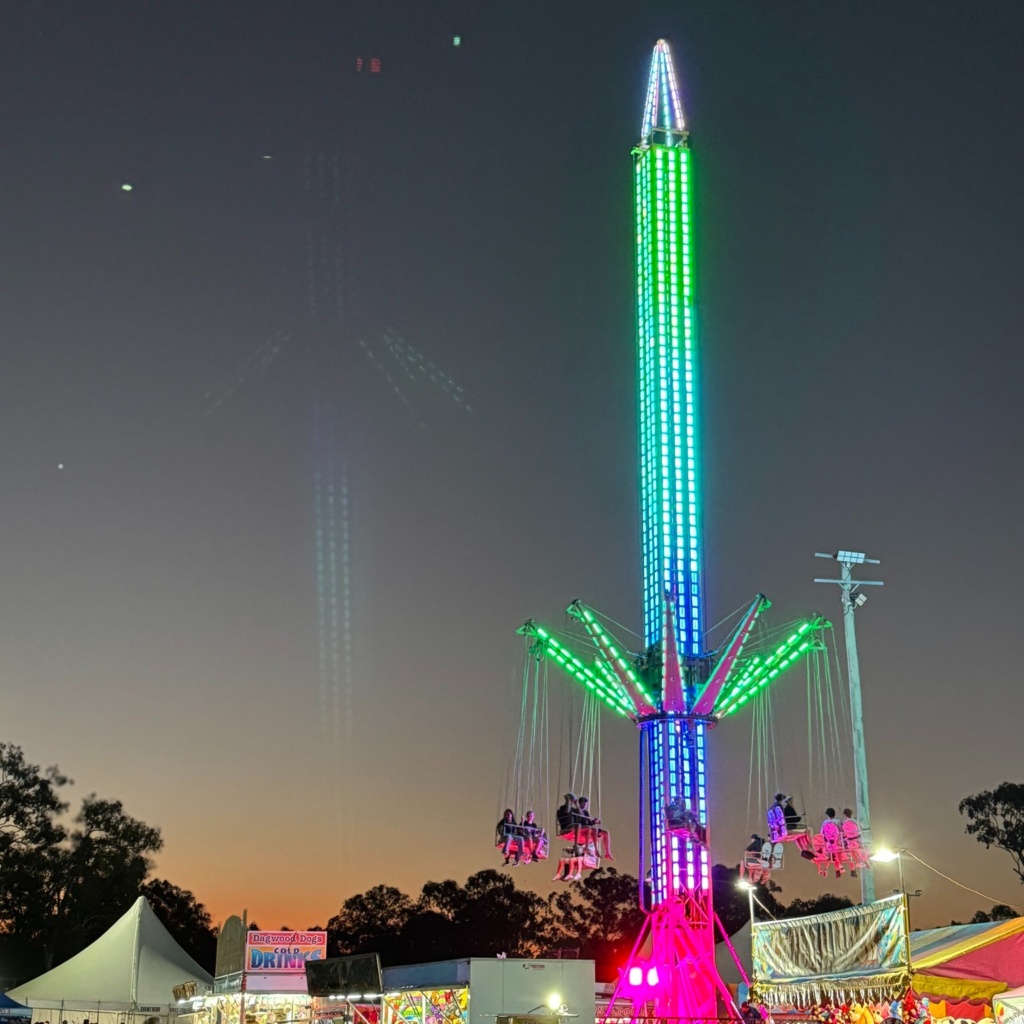

RedFest is Redland City’s main event, showcasing musicians and artists from across the region. For two days, the Redlands Showground becomes a celebration of the amazing community, with performers sharing their skills across the showground. Families are also taken care of, with a children’s program, featuring a range of free activities including farm animals, puppet shows, rock climbing and free face painting, Sideshow alley and spectacular fireworks.
The date is still in the works, check RedFest’s social media channels for date confirmation.
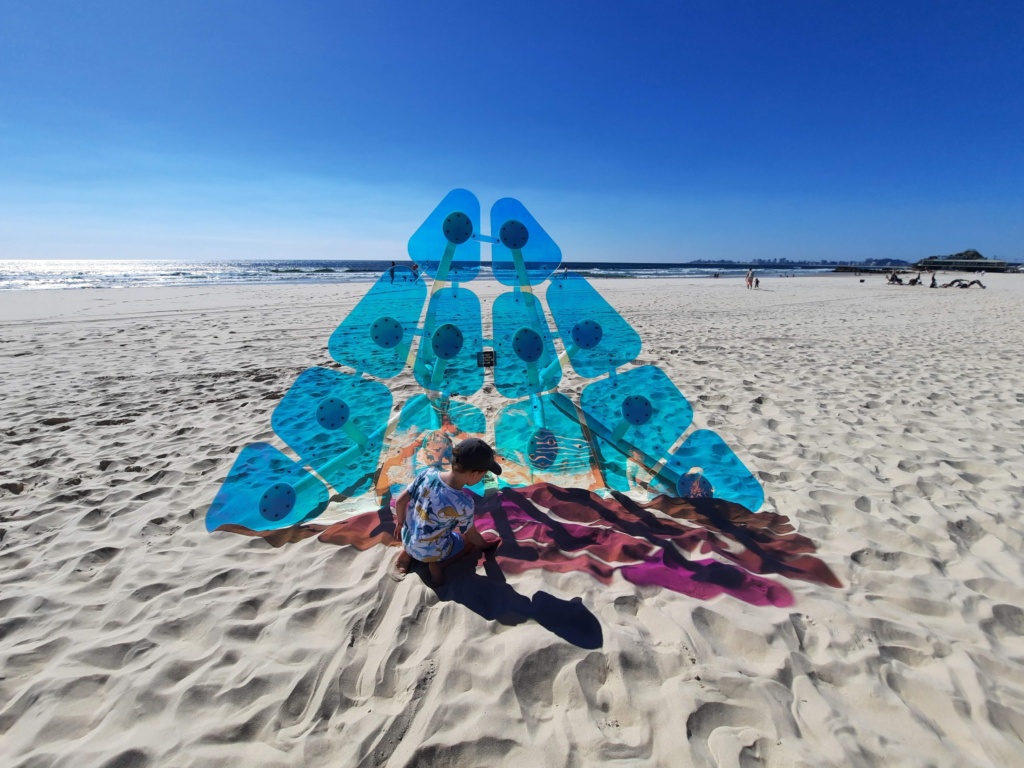

SWELL is Queensland’s premier outdoor sculpture exhibition, set along Gold Coast’s Currumbin Beach. For 10 days, more than 60 small, medium and large-scale sculptures will be set up along the beachfront and boardwalk for families to view.
The Family Zone activation is always popular, with workshops, activities, a BookFest setup where children can take home a free pre-loved book, live music and chill out zones set up under the leafy trees. Go at sunrise or sunset to beat the heat and experience the sculptures in a different light.
When considering how to look after your family during the work week, look no further than Little Scholars!
We offer your child the very best facilities, resources and early educational, play-based programs available, which are underpinned by the early years learning framework. We also believe in fun, wide-ranging experiences so that children can begin to develop interests and passions of their own, from Bush Kinder adventures to our broad extracurricular program which includes swimming for our kindergarten children, we believe in keeping wonder and magic in childhood.
Find Lara’s recommendations at her website Mrs. Lardeedah.com, and follow her socials Facebook and Instagram

The festive season is here and the opportunities to get in the spirit are endless! Why not check your shopping list off at a Christmas market, jingle along at a carols concert or putt your way through a Christmas wonderland. To make sure you do not miss out on the festive cheer, here is your go-to guide with only the best of the best Christmas happenings picked out for you. Be sure to add these dates to your calendar!
Get ready for an exciting and interactive Santa show! Join Santa, Mrs Claus and Rudolf for a Christmas extravaganza that includes a mix of traditional carols and current pop songs.
Pacific Pines Central Park, 4-8:30pm
Image via City of Gold Coast
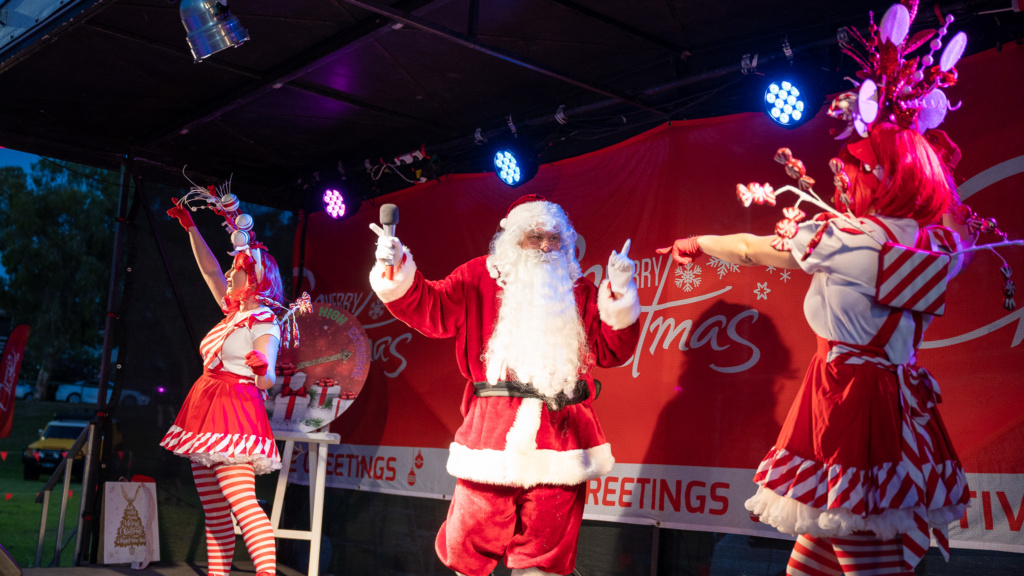

This free family festivity will feature live music, market stalls, inflatable fun, local restaurant specials, games and activities, plus a visit from Santa Claus.
Ron Short Park, 4-8pm

Bring your family for the largest carols event on the northern Gold Coast, an unforgettable night with fireworks, food vans, and festive sing-alongs.
Brien Harris Oval, from 4pm
Image via Northern Gold Coast Carols Facebook page

One of the all-time favourite Christmas carols will be performed in a 2-hour celebration of song and dance on the beach, with a visit from Santa, and a fireworks finale!
Surfers Paradise Beach, 5-8pm
Image via City of Gold Coast
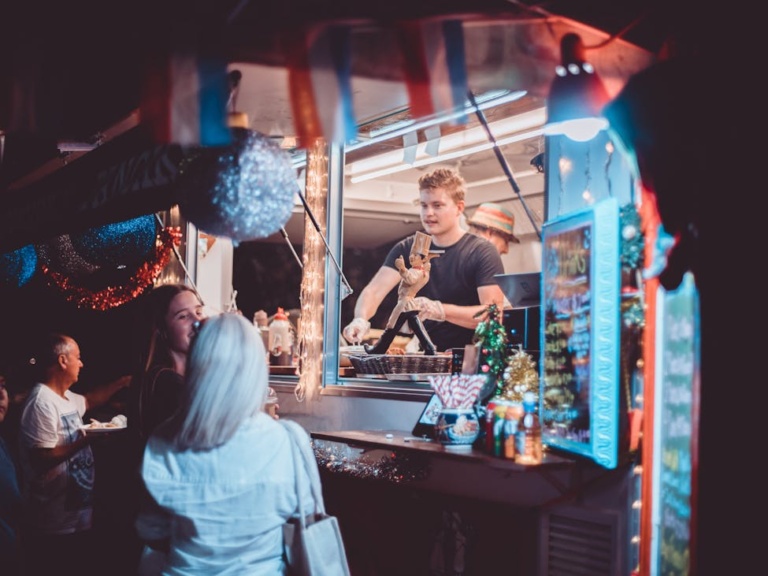

Wind your way through the Market lanes to the sweet serenades of stunning live music, spot roving performers, snap a selfie with an elf… or meet Santa himself!
Home of the Arts, 4-9pm
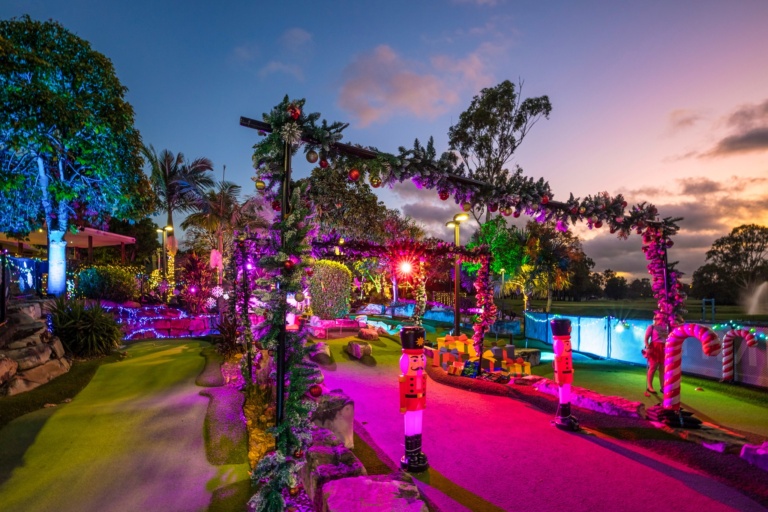

The elves have been busy transforming the 9-hole mini golf course into a spectacular Christmas wonderland!
76-122 Napper Road, Parkwood
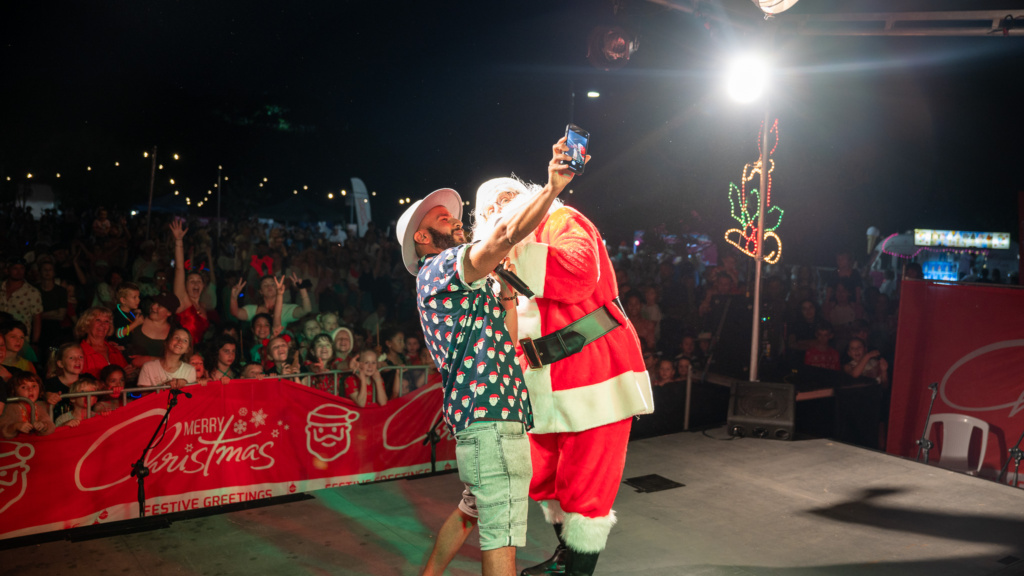

Free live music on stage, roving performers, children’s entertainment, fantastic food trucks, and Christmas market stalls. Plus see Santa making a special appearance alongside a fireworks display.
Ed Hardy Park, 4-8pm
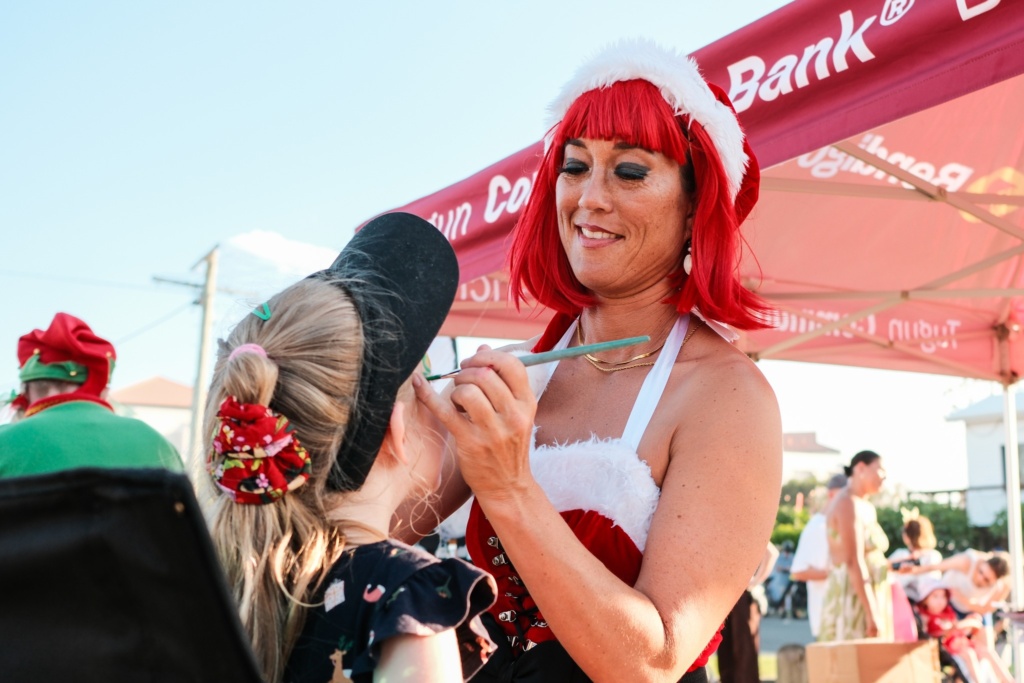

Dine under the stars at one of the fantastic local eateries, check out the local business offerings, and visit the Christmas market stalls. Plenty of free children’s entertainment on offer throughout the program with Santa making a special appearance!
Toolona Street, Tugan, 4-8:30pm
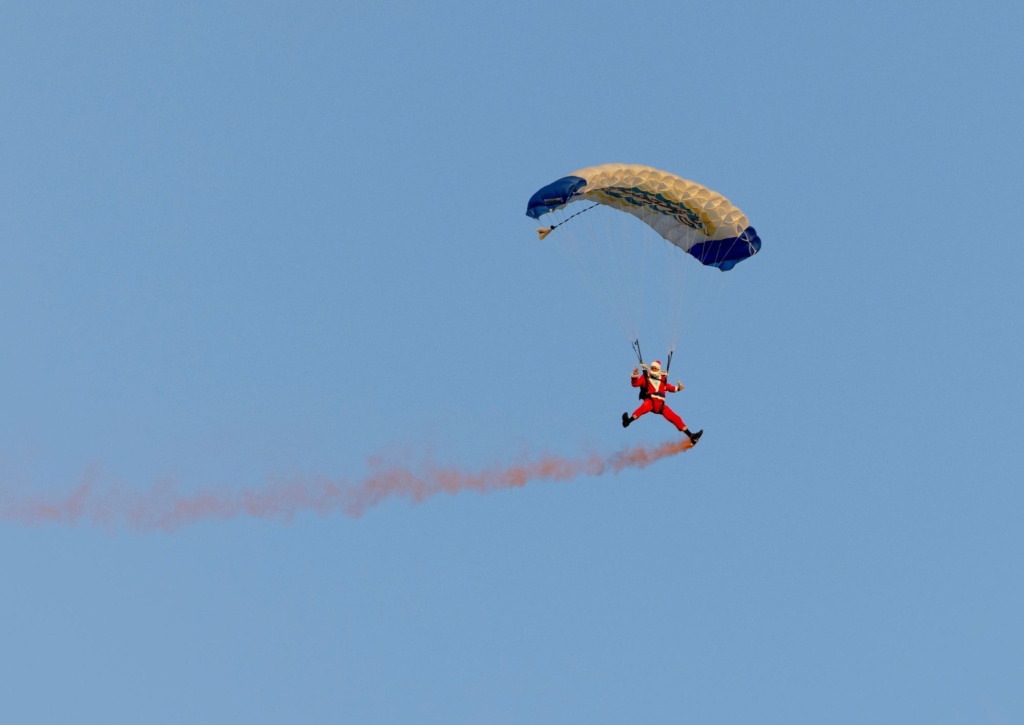

Sing along to your all-time favourite carols, enjoy a delicious assortment of food trucks, watch Santa fly in and watch a sparkling fireworks finale!
Queen Elizabeth Park, 5:30-7:30pm
Image via Shutterstock
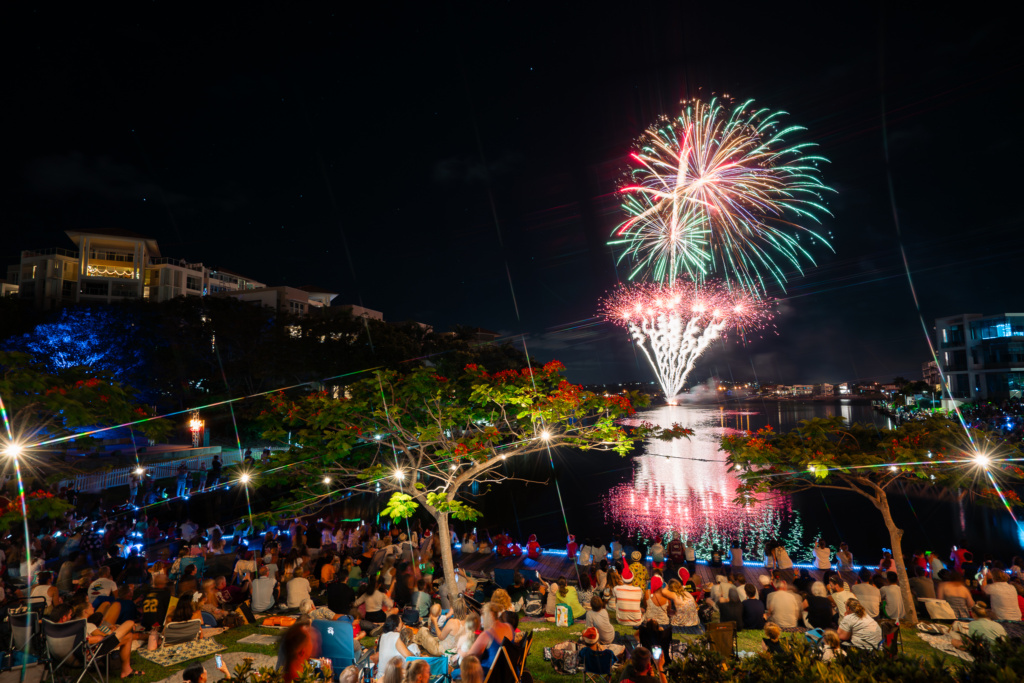

A truly unique festive celebration, this event will feature live stage entertainment, Christmas carols, Santa, Fireworks over the beautiful Lake Orr and much more!
Waterfront Stage, Varsity Lakes, 4-8pm
Image via Carols on the Lake Facebook page

A fabulous, family Christmas event with market stalls, food trucks, Santa, Christmas carols, live music, facepainting and free children’s craft area.
Mudgeeraba Showgrounds, 3-8pm
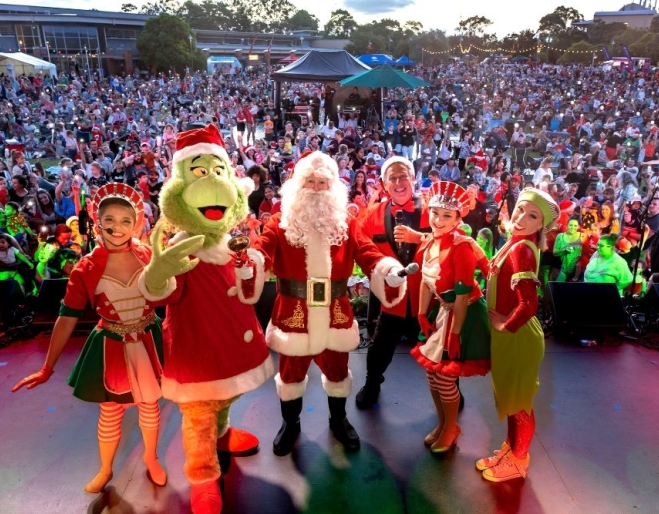

The City of Logan Christmas Carols is the city’s biggest annual Christmas event. This free, family-friendly event features hours of on-stage entertainment, festive activities, food trucks, and markets, all jam-packed into one magical day.
Kingston Butter Factory Cultural Precinct, 3-8:30pm
Image via Must Do Brisbane
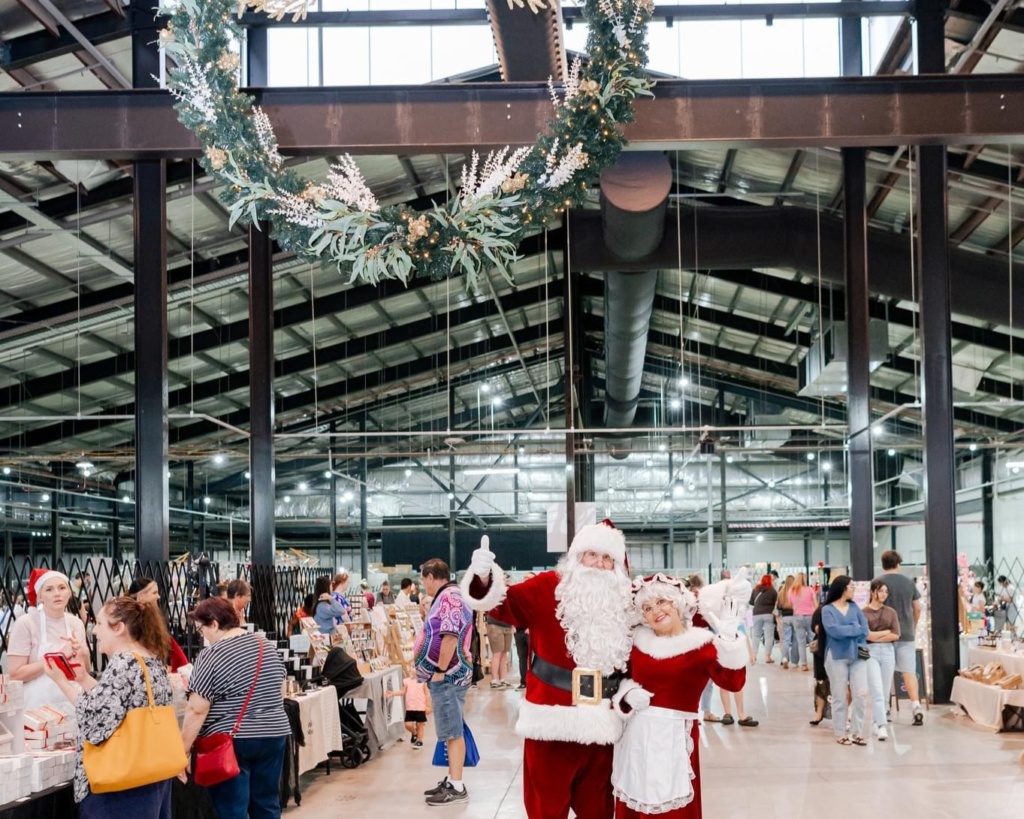

Experience a pop-up Christmas market brimming with a variety of local vendors, a special visit from Santa’s elves, and Mr & Mrs Claus will drop by for photos under a larger-than-life wreath, suspended above the Market Hall.
Distillery Road Market, 11am-9pm
Image via Facebook event

A free 7-minute light and sound show running at 6:30pm, 6:45pm, 7pm & 7:15pm. Get ready to catch all the “bubble snow” at the end!
Image via Redland Performing Arts Centre
If you’re looking for early education and care for your young family, look no further than Little Scholars!
We offer your child the very best facilities, resources and early educational, play-based programs available, which are underpinned by the early years learning framework. We also believe in fun, wide-ranging experiences so that children can begin to develop interests and passions of their own, from Bush Kinder adventures to our broad extracurricular program which includes swimming for our kindergarten children, we believe in keeping wonder and magic in childhood.
Find Lara’s recommendations at her website Mrs. Lardeedah.com, and follow her socials Facebook and Instagram


Grandparents have always shared a special bond with their grandchildren, but nowadays they are also playing an increasingly important role as a caregiver, as children spend much more time with their grandparents than ever before. Sometimes however, the generation gap can make it hard to think of new and fun things to do together that appeal to everyone.
Whether the grandchildren are spending an afternoon, a weekend, or the school holidays with you, this list is sure to keep children and grandparents of all interests and physical abilities, entertained and making memories year-round.
A beautiful day on the Gold Coast’s waterways make for some stunning views and great sight-seeing! The Gold Coast’s very own hop-on hop-off ferry is the perfect multi-generational way to spend a day. Departing hourly from five iconic Gold Coast destinations, including the famous Surfers Paradise and HOTA, Home of the Arts, you can hop on at any of the five stops, and stay aboard for the full loop (two hours) or explore the hop-off destinations at your leisure. Enjoy a drink from the onboard bar whilst the friendly captain keeps you entertained with informative commentary, music, local tips and wildlife spotting. Children can also meet the captain and have a turn driving the boat. There are a range of ticket options available, from day passes to long hops and short hops – depending on your budget and timeframes. Children under five always travel for free too!
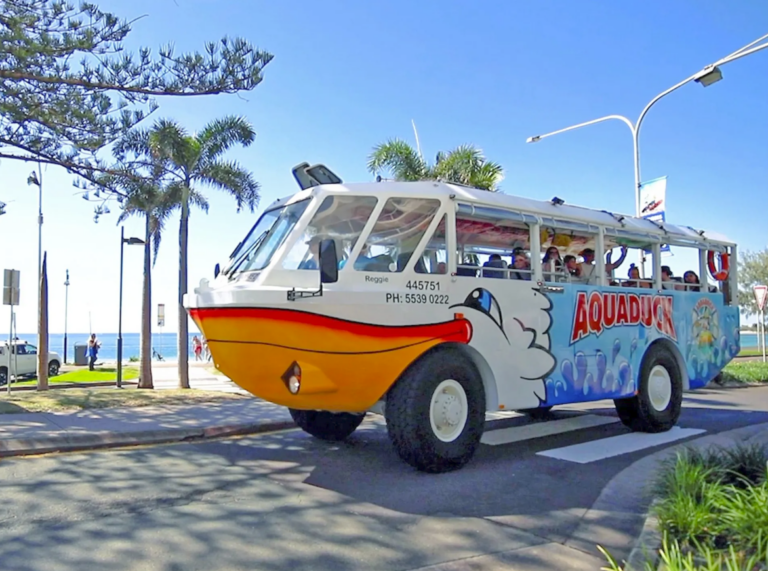

Another way to take to the water is with the iconic AquaDuck, and while it’s touristy, it’s a really great family outing, and perfect for multigenerational passengers. Embarking in the heart of Surfers Paradise, drive down the Esplanade overlooking the beautiful beaches and head towards The Spit. Once you reach the boat ramp just past SeaWorld, the tour changes pace and you’re heading for the water! Watch as the amphibious ‘duck’ changes from bus to boat and gently glides into the water. Now you’ll head through the Broadwater to check out how the millionaires live. You’ll finally return to land and drive down Tedder Avenue, before finishing back up at Cavill Avenue. The tour takes about an hour and is very family friendly, with children offered the chance to drive the boat and get their Captain’s certificate!
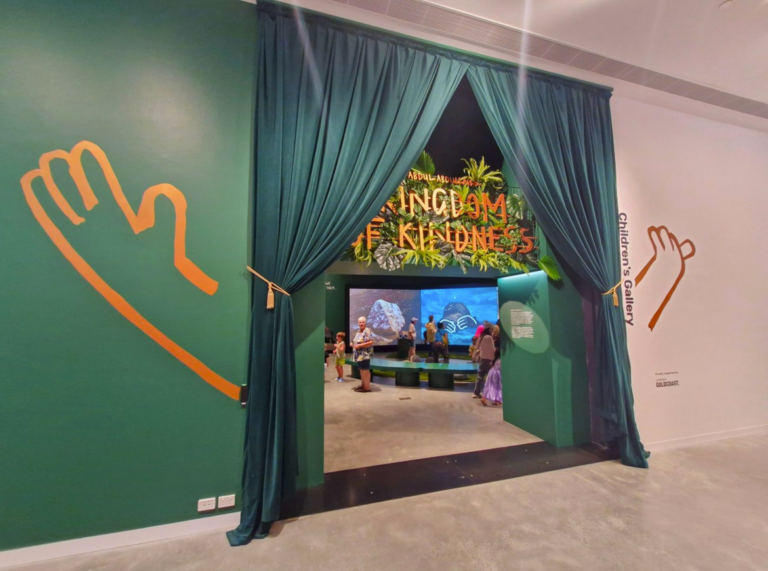

While the HOTA Gallery may be designed to cater for international art exhibitions, grandparents looking to give the grandchildren some culture will feel right at home! The Children’s Gallery at HOTA Gallery lets little artists get hands on – you won’t find any “do not touch” signs here! The Children’s Gallery changes every few months, each time offering a variety of interactive exhibits that complement the main galleries. After visiting the Children’s Gallery, take a stroll through the other free Galleries where you’ll find a few installations that are interactive and the children will love. Be sure to also ride the lift to the top floor and take in the Gold Coast skyline view! Fabulous 270 degree views await and there’s a guide you can use to work out what all the buildings are.
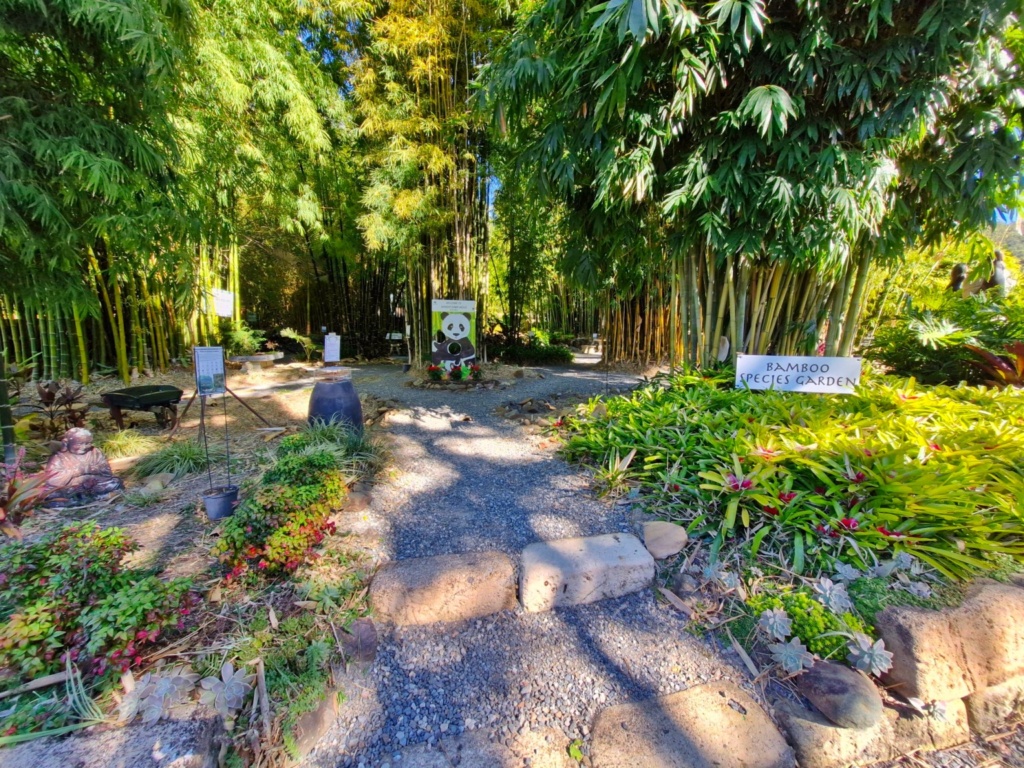

Bamboo Down Under at Wongawallan is a garden centre with a difference. The perfect grandparent’s day out, here you can explore a species garden, meditation garden, labyrinth, sensory garden and bamboo tunnel, and get bamboozled in the bamboo maze! Children can take on the Scavenger Hunt to discover the hidden pandas, all the while having a look at some incredible ornamental species of bamboo. Don’t miss the Rainforest Walk, a very peaceful stroll through a forest of enormous bamboo varieties. Dotted throughout are information signs about bamboo, little panda ornaments and other garden statues. Don’t miss the enchanted hollow at the end of the Tunnel.
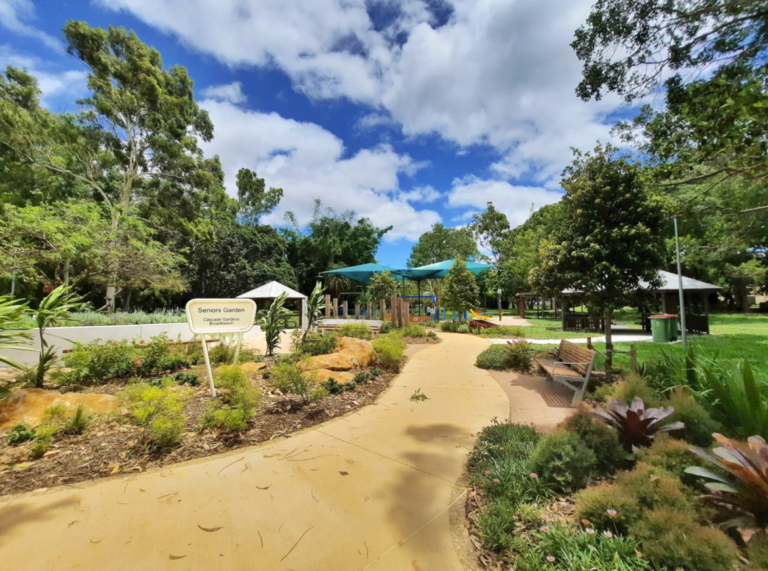

The Cascade Gardens at Broadbeach has a special addition of a sensory garden designed for seniors, but it also makes for great fun for little ones! In the sensory garden you’ll find elements including a musical gong, wayfinding design and productive gardens that encourage you to interact with the gardens through sight, touch and smell. It’s a beautiful addition to the Gardens and makes this spot perfect for multi-generational get togethers! The playground is older in style, but the children don’t seem to mind. You’ll find a flying fox, rope bridge, rock climbing wall and a carousel.
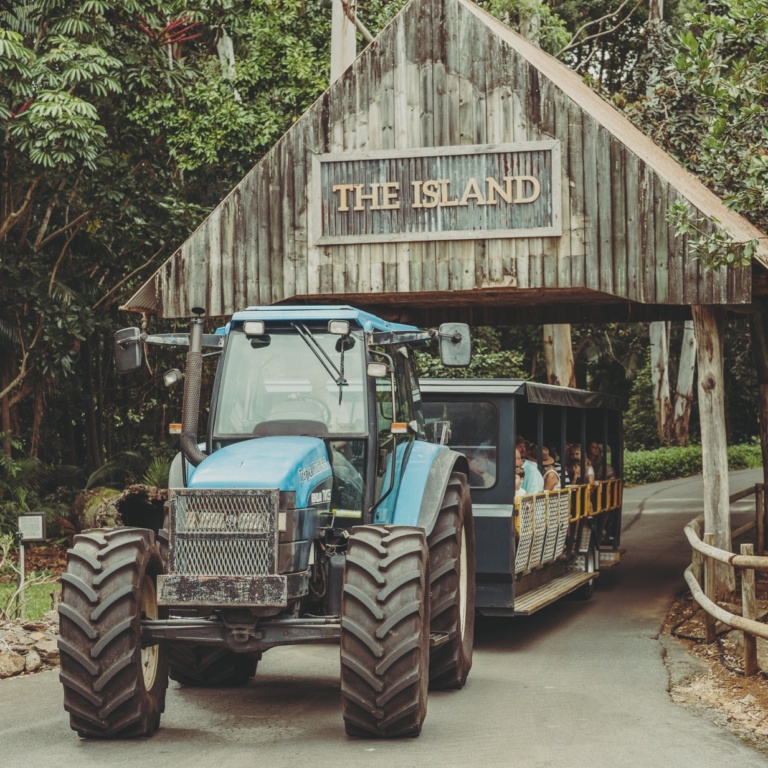

For the more active grandparents, a visit to Tropical Fruit World just over the NSW border in Duranbah is a fabulous day out for the family! Book a Farm Tour and experience a fruit tasting and a tractor-driven guided park tour. On the tour you can pick and eat bananas straight from the tree, crack macadamia nuts, feed and pat kangaroos, sheep, alpacas and miniature horses, and enjoy a short wildlife boat cruise too! At the end of the tour visit Wildlife Island and burn some energy on the flying fox, mini golf course and volleyball court. Then, check out the fruit market, café, and the huge sandpit by the grassed lawn to relax. If you live in the Tweed, Gold Coast, Byron, Lismore and Ballina, you can purchase tours at a discounted rate.
(Image with thanks to Tropical Fruit World)
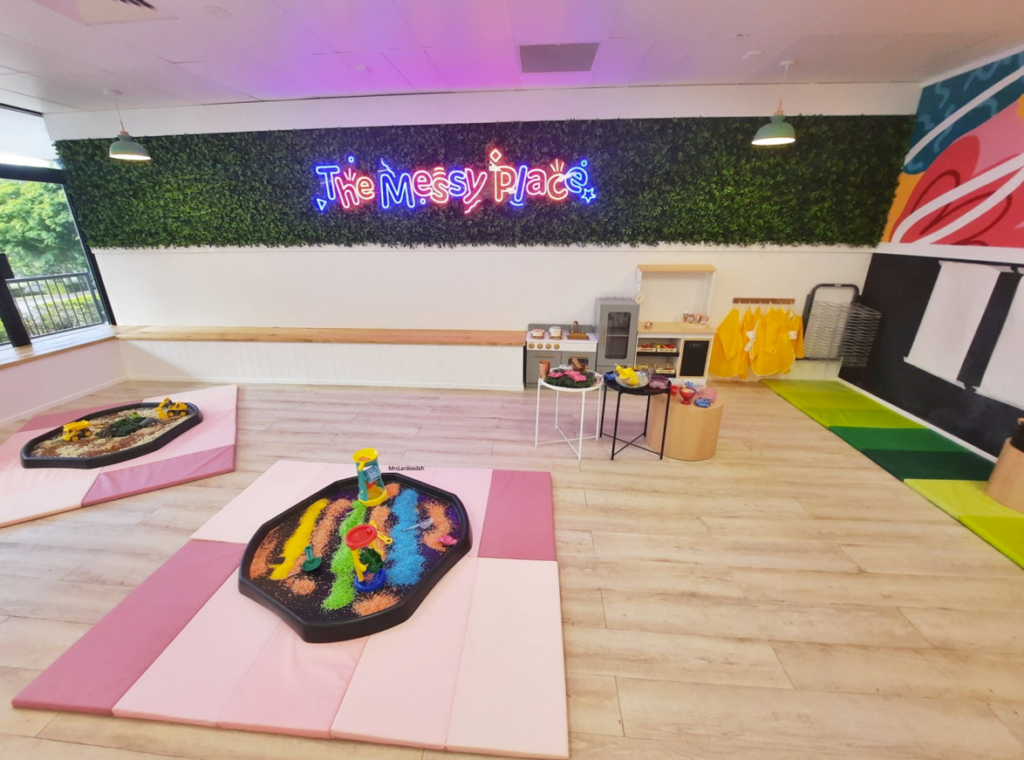

The generational gap can sometimes be hardest when the grandparents are tasked with spending time with energetic little toddlers. Keeping up with their ever-changing attention span, endless energy and natural curiosity is challenging for everyone! The Messy Place at Ashmore is the ultimate creative sensory play centre on the Gold Coast, designed exclusively for children under six years of age. They offer creative and messy play sessions in a safe and enjoyable environment, where they can unleash their imagination and make a mess. Exploration is encouraged, and grandparents can feel reassured being indoors in a secure, enclosed space. Sessions are booked on a casual basis and run five days per week.
National Grandparents’ Day is celebrated in Australia on the last Sunday of October. But as we all know, Grandparents Day is any day that the grandchildren can spend precious time with their grandparents. Whether you are a parent looking for how your child can have fun with grandma and grandpa or a grandparent seeking things to do with your grandchildren, we hope these ideas will inspire your time together.
We wholeheartedly believe in the proverb ‘it takes a village to raise a child.’ Little Scholars is proud to be a part of communities across South East Queensland, and we’re happy to play a small role in childhoods across the Gold Coast, Redlands and Brisbane.
We offer you and your child the very best facilities, resources and early educational, play-based programs available, which are underpinned by the early years learning framework. Our belief is that through quality education and care for children we can also encourage, assist and support the entire family.
Our dedicated team of educators are committed to the individual needs and interests of children and their families, and thus we encourage and welcome family input and involvement.
We aim to be like an extension of your family and are very relationship-driven. We support nurturing relationships between our educators and your child, the relationships your child has with the other children who attend, and we value our relationship with you as the parent and other family members. So book a tour today to get started!
Find Lara’s recommendations at her website Mrs. Lardeedah.com, and follow her socials Facebook and Instagram

While many Gold Coasters head to the southern suburbs on the weekend, the northern suburbs should not be overlooked for family-friendly weekend adventures! Starting in Stapylton and reaching to Pimpama, the most northerly suburbs of the Gold Coast also include Yatala, Alberton, Steiglitz, Gilberton, Norwell, Ormeau and Jacobs Well. Here you will find unique family activities, a range of family-friendly dining options, and some of the Gold Coast’s most unique play spaces. Here is your guide to getting the most out of a day in the Northern most parts of the Gold Coast.
South-east Queensland’s last original open-air Drive-In Cinema is located in Yatala, and boasts three massive screens accommodating up to 700 cars each night. Bring your camp chairs and sit out the back of your car to watch a movie, or bundle up the blankets, pillows and sleeping bags to make yourself comfortable in the back of your van, ute or car. Perfect for wriggly children, the privacy of sitting in your own vehicle means there is no need to worry if their bouncing around is bothering other cinema patrons. Movies screen every night of the week and they often host special event screenings too.
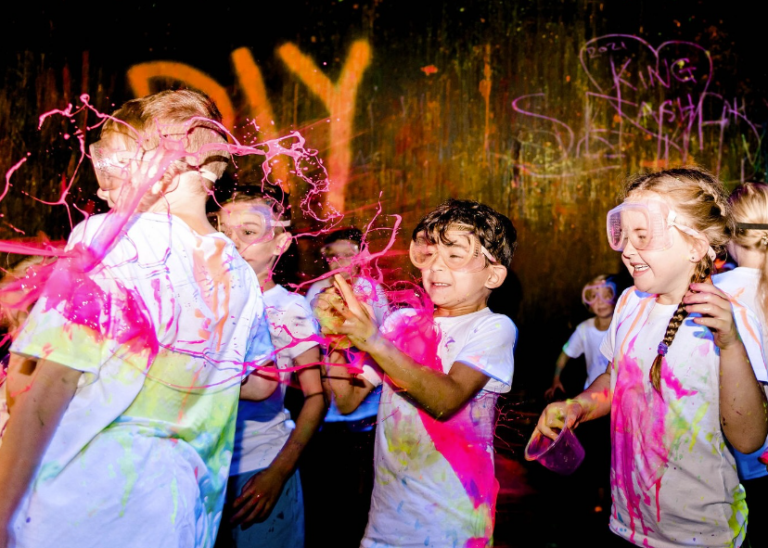
If your family is feeling creative, or looking to get messy, a workshop at DIY Invasion is sure to tick the box. Located at Staplyton, DIY Invasion run craft workshops ranging from resin art to painting, macrame and slime making – with their School Holiday Workshops always extremely popular for children. Another unique feature is their Splatter and Splash Room, which families can book for a private experience! Choose your own dance music, while letting your creativity run wild as you fling, flick, and splash paint around the room and over your fellow participants! This is a great space to unwind and tap into creativity.
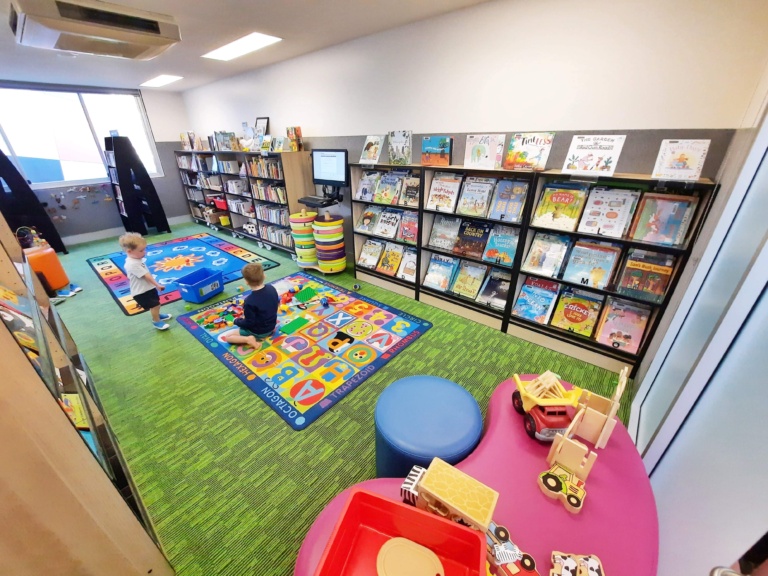

The only library located in the far northern suburbs, the Ormeau Community Lounge & Library is a hidden gem. Here you can visit the Gold Coast’s only Book Box corner, an early year’s library and play-based learning space delivered in partnership with Queensland State Library’s First 5 Forever program. Here children do not have to worry about being quiet, and they are actively encouraged to play with the many games and play resources available. Open six days a week, families can join in Story Time on Friday and Saturday mornings, or participate in Baby Rhyme Time and Toddler Time sessions during the week.
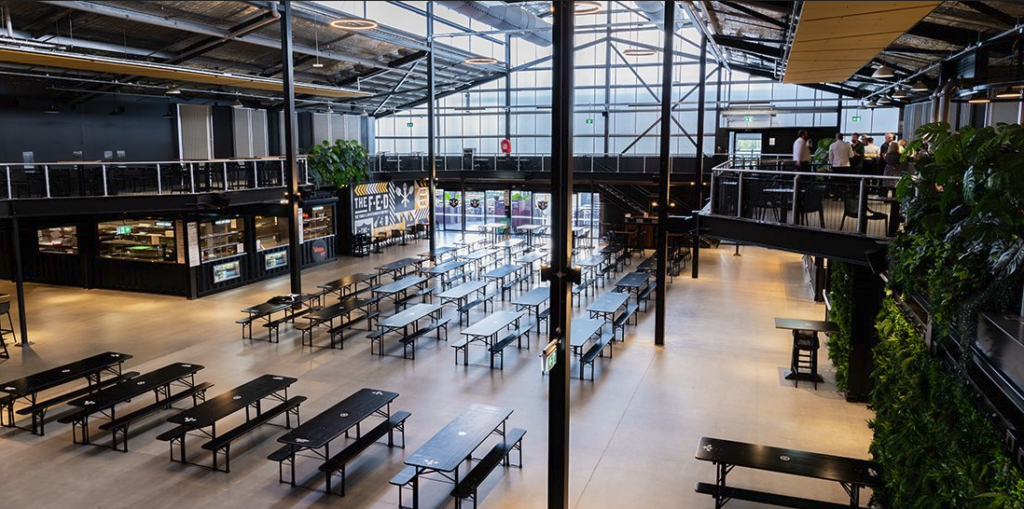

Distillery Road Market is a fresh and exciting new venue located in Eagleby, home to The F.E.D, a 2000-person food and entertainment space. Here you’ll find an expansive indoor/outdoor dining area, with a range of on-site eateries to choose from. Open Thursday – Sunday, the venue is family friendly with live music each evening and long beerhall-style tables to choose from. The best part is that diners can choose meals from six different food outlets, meaning that all tastes and dietary requirements can be catered for! The casual vibe of this venue is perfect for an early dinner with the family, where children and parents can relax, move around, dance and enjoy a great meal together.
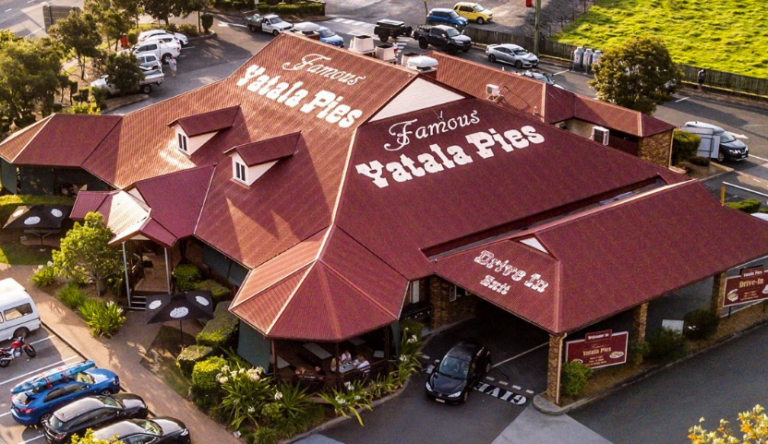

Yatala Pies has been a landmark in the Yatala area for more than 130 years, these days selling around 3,500 pies daily! Well known as a halfway stop on the journey between Brisbane and the Gold Coast, northern Gold Coast locals are lucky to have this icon right here in their backyard. Selling some of the best pies on the Gold Coast, the quality is exceptional and the range delicious. Choose from dine in or takeaway, you can grab a hot, ready-to-eat snack pie, or take-home, oven-ready family pies and snack pie packs. With something for everyone, the family will love a stop in at Yatala Pies any time of the day.
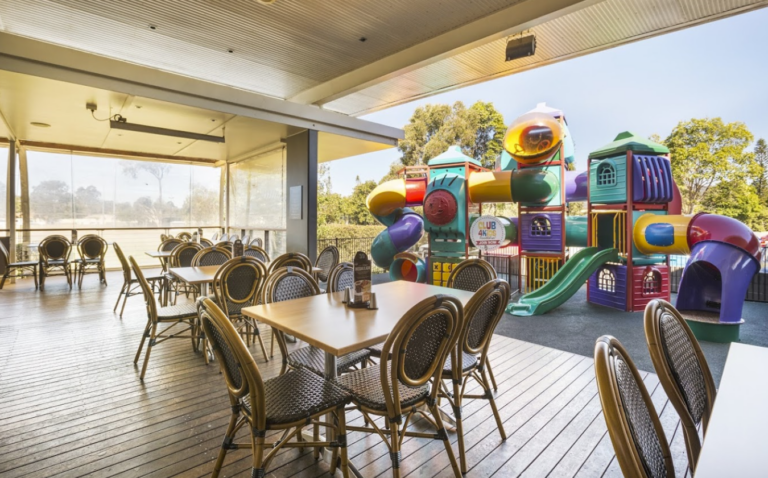

The Norfolk Tavern has got to be the most family-friendly dining option in the northern Gold Coast. Indoors you will find a bright and spacious dining room, while outside there is a wraparound veranda with ample space for dining, opening on to a huge children’s playground. The award-winning Bistro has menu options to suit every taste, from fresh seafood to steaks, pastas, salads and all the traditional pub fare. Extremely popular on weekends, be sure to book a spot on the deck if you are dining with children for easy line of sight from your table to the playground.
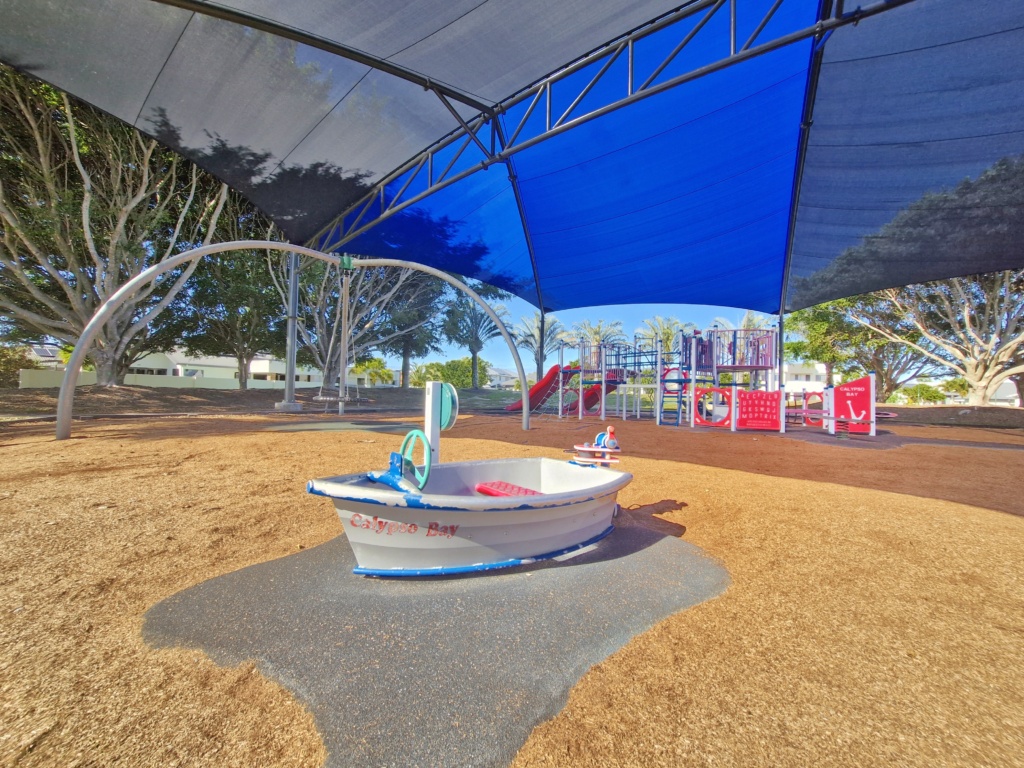

A nautical themed playground appropriate for its position by the water and close by the Calypso Bay Marina, here you’ll find a pirate ship brimming with bridges, wheels, slides and nets – be careful, you might even be asked to walk the plank! Underneath the pirate ship the imaginative play space is further extended, with a small shop counter set up, tunnel frames and other interactive game panels. The swing set with all abilities swing is always popular, as is the spinners and hammock swing. There’s also a little boat for children to pretend to fish or start the engine!

While many think the most northern beach area for children to swim is at Paradise Point, there is a lesser-known spot at the very northern edge of the Gold Coast – Lions Park at Jacobs Well. With easy access from the carpark, you are at a small, shaded beach in just a few steps. The swimming enclosure here has a small sandy beach, a large shade sail over the sand, and few waves, making it ideal for toddlers and younger children gaining confidence in the ocean. Parents will love the ability to sit on a blanket under the shade and still be close enough to their children in the water.
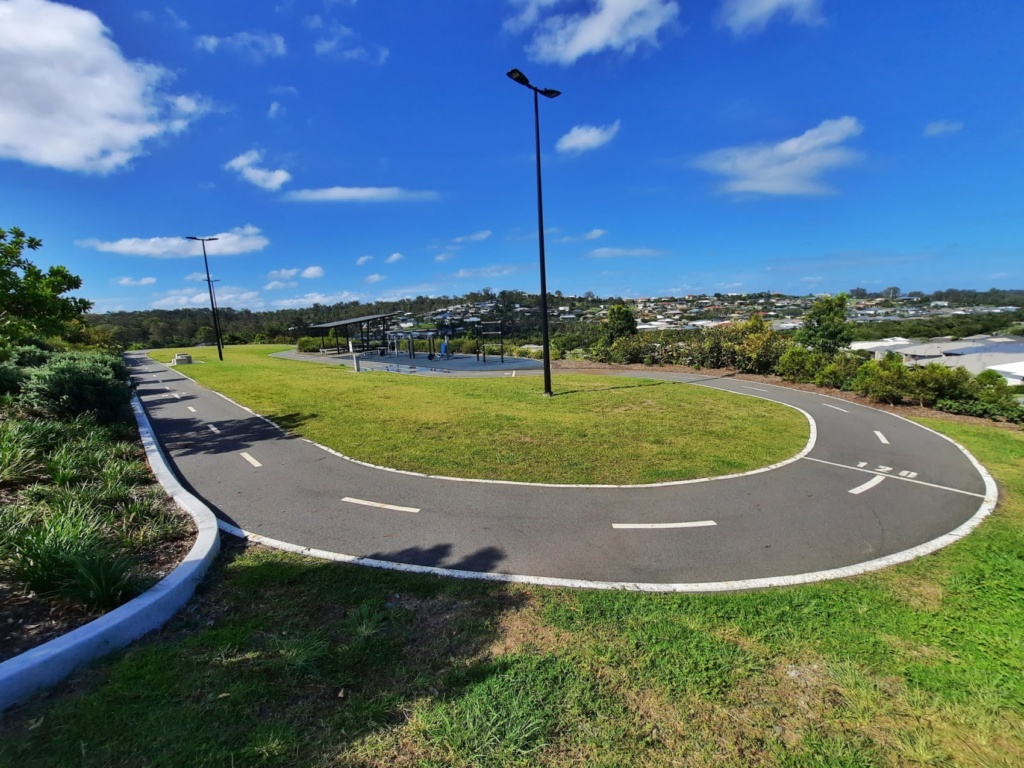

While the playground at Outlook Park, Ormeau may be tiny, pack the bicycles and prepare yourselves for the surprise bike tracks that make this a fabulous spot to visit! Set on a steep slope, Outlook Park is laid out over three levels. At the top you’ll find a small playground best suited for toddlers, and then on the middle and lower level there are two bike tracks, perfect for racing on. While the playground is very small, the bike tracks are great for bicycles, skateboards or scooters, and children will love lining up at the start line and racing the loops to the finish. Celebrate with some pretend play medal ceremonies on the dais at the track!
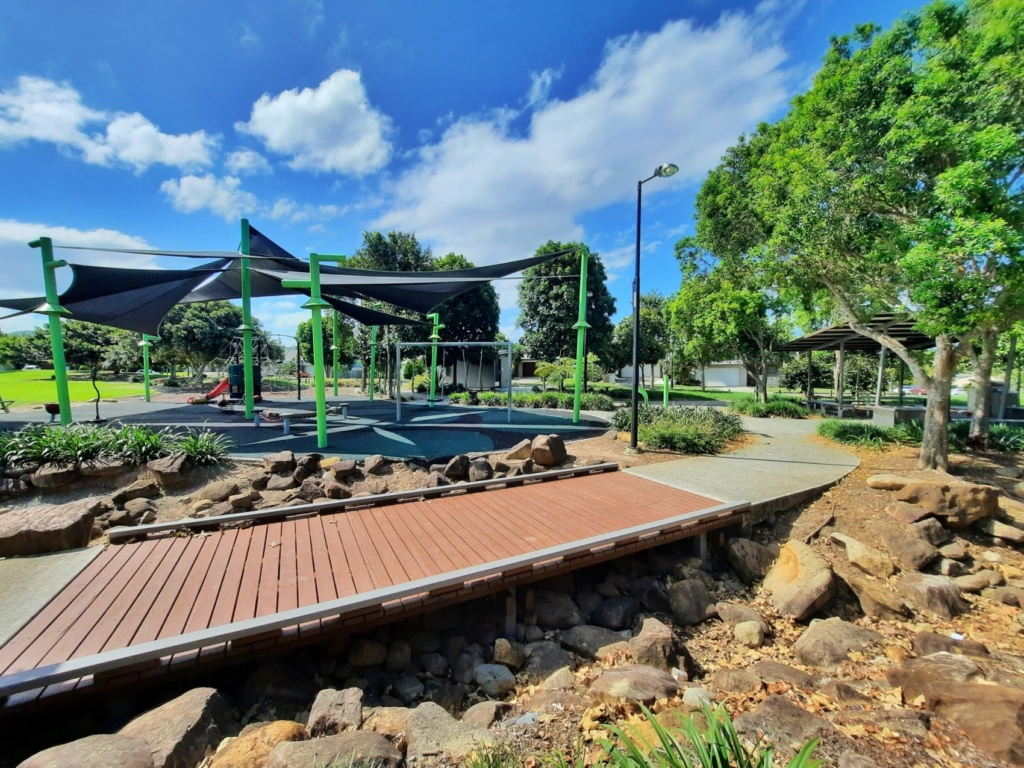

Hilltop Park in Ormeau is an older park, but still delivers a great time. Split into two sections, toddlers will love the smaller, shady play area with a car, climbing frame and mini playground with slide and swing. The main playground space is better suited for children over five, with a larger playground and slide, large climbing net, balance beams, spinners and swings. Children can also climb the ramp up to the old water tower, which has been converted into a play structure.
The northern Gold Coast offers a variety of unique and exciting activities for the whole family. From classic drive-in movies to hands-on creative workshops, scenic playgrounds, and delicious dining options, these suburbs have something for everyone. Whether you’re looking for a relaxing day by the water or a more adventurous outing, there’s no shortage of fun to be had. Next time you’re planning a family day out, consider exploring the hidden gems of Stapylton, Ormeau, Yatala, and beyond—you might just discover your new favourite weekend spot!
Little Scholars provides quality early education and care for children across South East Queensland, including five early learning campuses in Stapylton, Yatala and Ormeau.
We offer your child the very best facilities, resources and early educational, play-based programs available, which are underpinned by the early years learning framework. We believe that through quality education and care for children, we can also encourage, assist, and support the entire family.
Our dedicated team of educators are committed to the individual needs and interests of children and their families, and thus we encourage and welcome family input and involvement.
Find Lara’s recommendations at her website Mrs. Lardeedah.com, and follow her socials Facebook and Instagram

The Gold Coast is known for its abundance of good food and stunning dining options, but when you have young children in tow – often the thought of dining out can be daunting. Thankfully, many local restauranteurs have heard the call of parents seeking family-friendly dining options. We’re now seeing dining venues with amazing menus, family-friendly fit outs and features to help keep the children occupied while you enjoy a hot meal. Whether it be a playground, a simple children’s corner, or open spaces to move around safely, there are plenty of choices for you to enjoy your next meal out. Here are my top six family-friendly dining venues on the Gold Coast that you should be sure to visit!
This shopping centre café is a hidden gem, saving the sanity of parents for many years now. With opening hours stretching from 5.30am – 9pm, you can often find those parents with early-risers enjoying a hot coffee at Café 63 in the early hours. Located in the incredible “Backyard” precinct at Westfield Coomera, the outdoor dining area overlooks a fun-filled obstacle course with adventure play suited to four-eight year olds. For the youngest children, a nearby splash pad and toddler sensory zone also serve as great spaces to stretch the legs while waiting for your meals to be served. The menu here is extensive and well-priced, including a fabulous children’s menu that will please everyone.
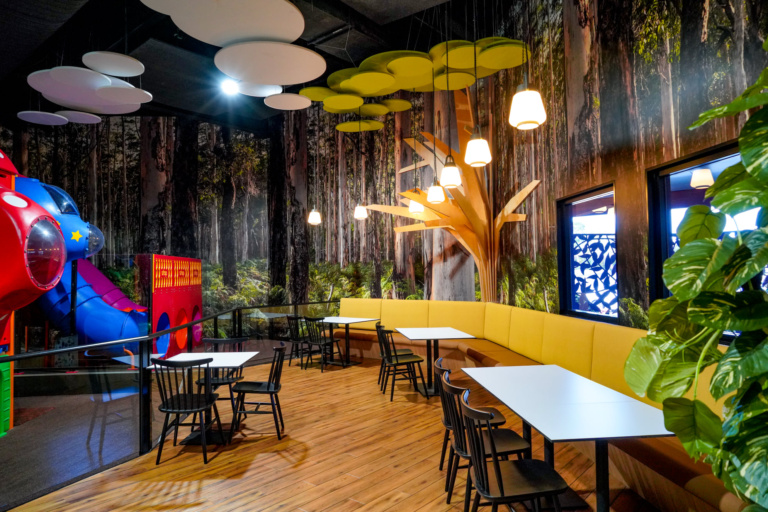

Here you will find a huge indoor children’s playground for four-12 year olds, with a family specific dining space attached. Separate from the rest of The Wattle Hotel’s restaurant, this glassed-off dining room overlooks the playground and contains about 15 tables. Here children can easily move back and forth between the playground and the table while their parents can see them at all times. There is a great children’s menu and delicious daily specials to enjoy, this is modern bistro dining that can be enjoyed by all the family.
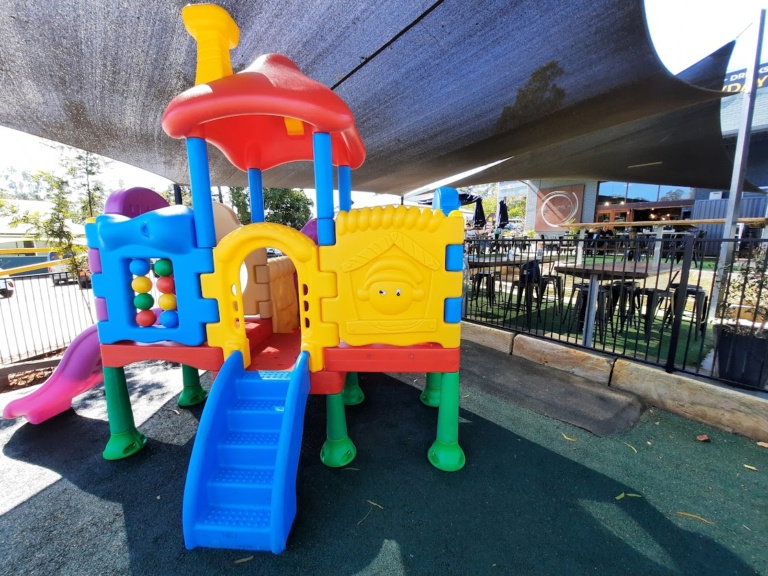

A café best known amongst the Coast’s cyclists thanks to its location near the Velodrome and bike shops, Cadence Café also caters beautifully to families seeking great food. Set across three terraced levels, the venue is connected by a central path and steps – at the top is the café, the middle level has plenty of dining tables and chairs, and the lower level is home to high bar tables overlooking a fenced children’s play space. All levels are shaded by a beautiful fig tree, have ramp access, and dogs are also welcome in the outdoor areas. Serving breakfast and lunch, the menu caters well to families, and you are sure to enjoy a delicious meal.
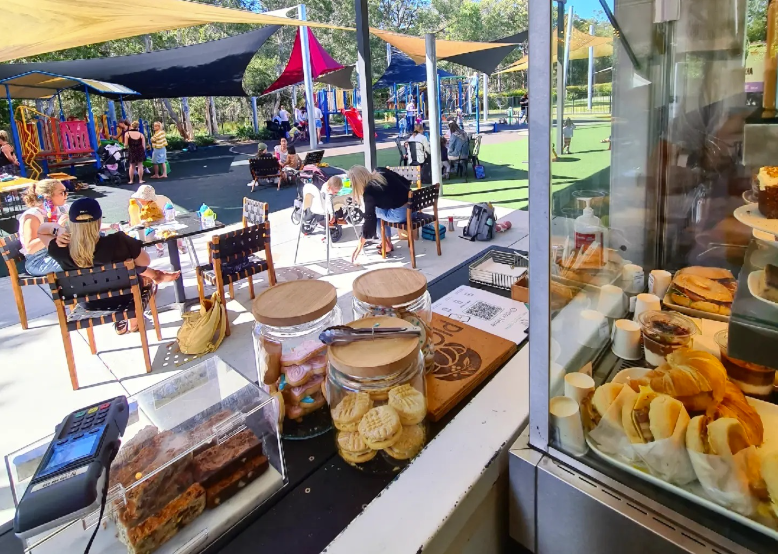

Just off the hustle and bustle of Olsen Avenue sits the Latte Lounge, a family-friendly oasis amongst the gum trees. Here you will find house-roasted specialty coffee and a delectable brunch menu, plus one of the best children’s menus you will find at a café. The open-air café is almost the second-best attraction, when you see the large, easily accessible playground right in the middle of the café. Designed for all ages, this fenced café and playground is covered by large shade sails and offers plenty of shady spots to enjoy your meal. With its central Gold Coast location, this is also an extremely popular spot for birthday parties and play dates. Thankfully, due to the size of the café and playground it never feels overly busy or crowded and is always a delightful outing.
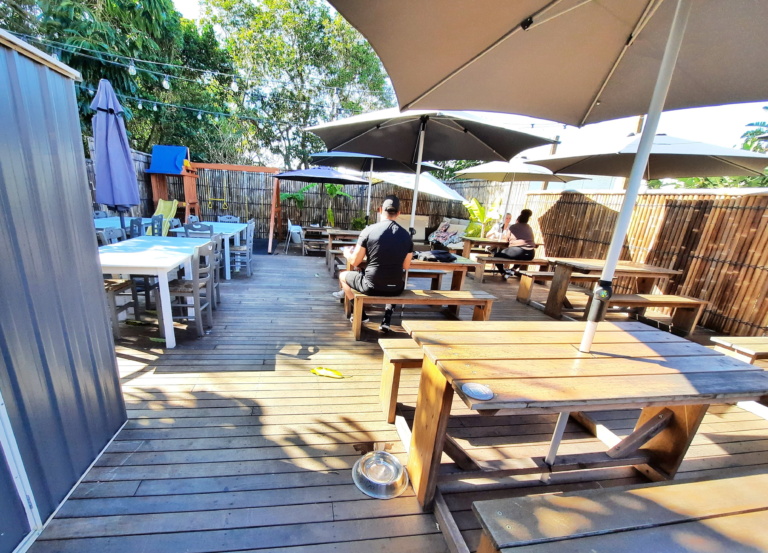

This hidden gem on the southern end at first appears to be a juice bar, but venture inside and you will find a breezy indoor/outdoor café with children’s playground! Popular with the locals, this unassuming little spot is filled with sunshine, great food and service with a smile. This is a family-run café with its roots in healthy superfoods that taste phenomenal. Dog friendly, the outdoor deck is the place to be, with easy line of site to the children’s playground. The café kitchen is only open Thursday – Monday, but the juice and smoothie bar is open 7 days.
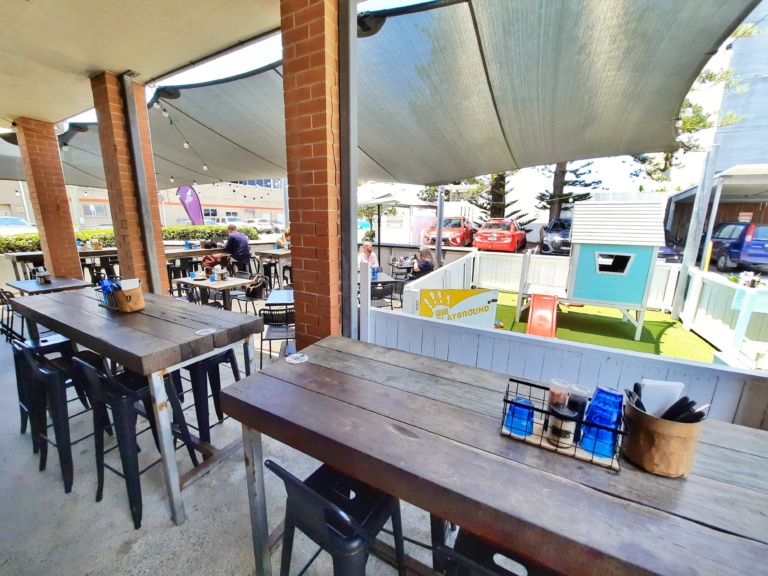

With beautiful coastal vibes, indoor/outdoor dining is essential on the Gold Coast, and BSKT serves it up perfectly. Located just steps away from the beach, BSKT has delicious food, ample seating and a fenced children’s play area. Pronounced biscuit, this menu is packed with vibrant colours and bold flavours, but also caters well to children. BSKT doesn’t take books and this spot is extremely popular on the weekend, but wait times are usually short. Be sure to grab a spot outside under the patio to have easy access to the play area! Why not pack the swimwear and walk over to the beach afterwards!
Find Lara’s recommendations at her website Mrs. Lardeedah.com, and follow her socials Facebook and Instagram
Children’s positive views of themselves as learners are more important than being told they are clever.
This insight from Nathan Wallis’s talk at the Australian Childcare Alliance (ACA) conference resonated with us, and we believe it’s valuable for parents to hear. Our intention isn’t to make parents feel guilty for praising their children’s intelligence. We understand that parents aim to foster a strong sense of self and ability in their children, and we fully support this. However, Wallis emphasises that before the age of seven, children don’t need to prove their intelligence. Instead, they need to develop learning skills through play and believe in their ability to learn. According to Wallis, more play and less structured learning before age seven leads to better outcomes in adulthood.
“To put it simply, before seven, it doesn’t matter how clever your child is. What matters is how clever your child feels and their disposition towards themselves as learners,” Wallis, an educator who focuses on neuroscience, explained on the Future Focus podcast.
“You’re better off having a six-year-old who can only count to 20 but thinks they’re a good learner than a six-year-old who can count to 100 but doubts their cleverness.”
Wallis highlights that free play boosts creativity and problem-solving, which are essential for intelligence. Letting children freely build, create, and explore supports flexible thinking and a positive learning mindset.
At the conference, which attracted hundreds of early childhood educators, Wallis offered advice on how to support children in their confidence and ability to learn:
Experts at Early Childhood Australia agree that children learn about themselves, others, and the world around them through play.
“If you provide your child with plenty of opportunities for playing, exploring, discovering their interests, solving problems, and tackling challenges, then you’ll be laying a strong foundation for building self-confidence,” says David Lyons, CEO of Nido Early School, in a post on ECA’s The Spoke blog.

According to Be You, the national mental health and wellbeing initiative for learning communities in Australia, praise is most effective when adults are mindful of how and when they use it.
When praising children, Be You suggests focusing on their efforts and achievements.
“Praise that’s specific and acknowledges the process of completing an activity or solving a problem helps develop children’s learning and motivation. For example, you might say, ‘You put away your toys so nicely,’ ‘I noticed you were really trying hard at building that block tower,’ or ‘You’ve used so many bright colours in your painting.’ Children can then use this learning when they have similar experiences in the future.”
Lyons agrees and cautions against overpraising.
“Children need to discover and learn those things that give them personal enjoyment and fulfilment, not just do things to please their parents. Similarly, comparing a child to others can be detrimental to their confidence and self-esteem.”
Dealing with disappointment is also crucial for developing confidence.
“Everyone fails to achieve their goals sometimes – and this isn’t a bad thing. You can build children’s ability to deal with challenges by responding sympathetically and with encouragement, helping children focus on what they can change, and challenging ‘I can’t’ thinking by showing and saying you believe in them and reminding them of their achievements,” says Be You.
Wallis reinforces that play enables children to develop social, cognitive, and emotional skills through their own interests and in creative and innovative ways.
“Play-based learning teaches creativity, which is fundamental to growing intelligence and the ability to problem-solve. When children can take their time and make multiple attempts before achieving success, they build resilience and other important skills needed later in life,” says Wallis.
Supporting children in developing a positive self-view as learners is crucial, especially in their early years. Emphasising the importance of play over structured learning fosters creativity, problem-solving, and resilience. By providing nurturing relationships, paying attention to their efforts, and creating flexible learning environments, we can help children build the confidence they need to thrive.
As Nathan Wallis and other experts highlight, the goal is to make children feel capable and enthusiastic about learning. This foundation will benefit them not only in school but throughout their lives. At Little Scholars, we encourage our little ones to play, explore, and believe in themselves – because how they see themselves as learners today will shape their success tomorrow.
Everyday life is full of risks and challenges, and at Little Scholars, we believe children need opportunities to develop the skills associated with managing risk and making informed judgements about risks from a very young age. Risky play helps to develop important life skill learnings such as; building resilience and persistence, critical-thinking skills, self-confidence and even extends their frustration tolerance.
We get it—no one wants to see little ones get hurt. It’s almost instinctual to hover nearby in case they stumble or to call out ‘be careful!’ when they’re taking risks. But could this actually be sending the message that we don’t trust their capabilities or instincts? Historical trends show that since the 1960s, there’s been a shift in how we view children. Once considered competent, responsible, and resilient, the modern perspective leans more towards constant supervision and protection. What used to be unrestricted and often unsupervised outdoor play has transitioned to structured, closely watched, and frequently indoor activities.
A lot of research has been devoted around the world to risky or adventurous play, and how parental attitudes as well as other factors played a part in children’s activities.
By participating in adventurous play, children are more likely to engage in activities that elevate their heart rate and breathing, leading to increased energy expenditure. This can help children meet the recommended guidelines for MVPA, which is at least 60 minutes of moderate-to-vigorous physical activity daily.
‘Educators facilitate gradual exposure to controlled risks, allowing children to develop confidence and judgment, ultimately empowering them to make informed decisions when navigating different situations.’
-Kristen Guymer
Adventurous play also offers opportunities for children to develop and enhance their motor skills, coordination, balance, and strength. These physical skills are essential for overall physical development and can contribute to improved physical fitness.
Furthermore, adventurous play provides children with opportunities to explore their environment, take risks, and challenge themselves. This type of play promotes creativity, problem-solving, and decision-making skills, as children navigate and overcome obstacles. It also fosters a sense of adventure, independence, and self-confidence.
Overall, adventurous play can be a fun and engaging way for children to meet their daily MVPA requirements while promoting physical fitness, skill development, and personal growth.
“We emphasise the importance of careful observation, encouraging children to identify potential hazards by looking, listening, and even touching when safe,” she says. “Educators also foster critical thinking by asking questions that prompt risk assessment, such as, ‘What could go wrong if…?’ We promote collaboration and communication, allowing children to discuss and share their perceptions of risk.”
Furthermore, Kristen shares, educators facilitate gradual exposure to controlled risks, allowing children to develop confidence and judgment, ultimately empowering them to make informed decisions when navigating different situations.
Before embarking on Bush Kinder experiences or similar activities, educators guide children through risk assessments:
Hayley Yates, a lead educator at our Yatala campus agrees that discussions with children previously help prepare for and mitigate risk.
“We support risky play through our discussions with the children,” Hayley says. “If it’s something that has a big risk, example climbing trees, we talk about what we should look out for when climbing, how big the branches need to be to be safe and things of that nature. For both the younger and older children we use language like ‘Notice how this is this? Another example would be walking on slippery rocks, I would say ‘notice how that rock is wet? That might be slippery’, then giving them the option to continue to that rock or a different one.”
Hayley says through important discussions educators are guiding children by asking questions and role modelling safe behaviours.

At Little Scholars, we believe that spending time in nature has numerous benefits for children, including improved physical health and strength, enhanced cognitive development, and better emotional regulation. Through our Bush Kinder program, children have the opportunity to connect with nature on a deep level, learn about the environment, be challenged beyond the classroom, and engage in meaningful, hands-on experiences.
During our Bush Kinder sessions, children have the opportunity to engage in a range of activities, from nature walks and bird watching to building shelters and learning about indigenous culture. Children climb, scramble, jump and more in nature’s playground.
In this natural environment, children encounter diversity, novelty, challenges, and even some calculated risks. Their senses come alive as they engage with sticks, tree holes, water, rocks, sand, and dirt—nature’s abundant toys.
Our Bush Kinder educators are highly experienced and qualified in outdoor education and child development. They are passionate about providing children with meaningful learning experiences in a safe and supportive environment. We take the safety and security of our children very seriously. Our Bush Kinder program is conducted in a safe and secure outdoor environment, with strict protocols in place to ensure the well-being of all children.
But risky play is not limited to bush kinder.
Our outdoor areas are thoughtfully designed, including forts and equipment, all with intention of helping children navigate risk, endure challenges and build motor and fine motor skills.
Helena Vairy, an educator at our Ormeau Village campus, shares an example of how she helps children assess risk and how to complete ‘risky’ tasks safely.
“The way I like to teach children to access risk are by providing them with the materials which are needed and seeing how the children act on these,” Helena says. “
“The other week myself and a couple of the Kindergarten children set up the sandpit I placed the crates in a line and stacked one on top of the other. One child Mahli said ‘this looks like a runway maybe we can walk and then jump off the crates.’ What a great idea this was, the children were nervous at first but I stood right next to them to help. I asked the children, ‘do you think you can jump off the crated and land with your feet flat?’ I then demonstrated and the children too were off jumping.

We love this story because it shares how children lead their own learning experience, consider risks, and support and encourage each other.
All of our campuses have recently introduced woodworking stations, designed to help children exercise their creative and critical thinking skills. It allows them to express their ideas and figure out solutions to their projects. It’s also a great way to introduce risky play, as the risks are managed and educators are actively supervising, but woodworking teaches children about safety and understanding risk.
“As they pick up their hammers, they’re getting ready to work on their pincer grip,” says Katie, educational leader at our Parkwood campus. “Things like that prepare them for school. In order to prepare to help the children use these safely, we’ve been having group discussions and asking them different questions about how to use the tools, what they think the tools do and what they can make in the future.”
It’s clear that risky play isn’t just about letting children run wild; it’s a calculated approach to help them develop essential life skills. At Little Scholars, we’re not just about keeping your little ones safe; we’re about preparing them for life. Our educators are trained to guide children in assessing risks, making it a learning experience that builds confidence and safe judgment. So, parents, it might be time to loosen the reins a bit. Let’s trust our children to make informed decisions, even if it means resisting the urge to shout, ‘Be careful!’ every so often. After all, life is full of risks and challenges, and what better time to learn how to navigate them than in the formative early years? You’ll be amazed at what they can achieve when given the freedom to explore, assess, and conquer.
We know you want to give your child the best possible start in life. We foster nurturing relationships between our educators and your child, building and gaining their trust so we can support your child as they take on risks and challenges safely and confidently. Book a tour today to get started!
Further reading:
Did you know that clay is not only a fun material for children to play with but also incredibly beneficial for their development?
What’s fantastic about clay is its open-ended nature. There’s no right or wrong way to play with it, giving children the freedom to explore and express themselves. Whether they’re rolling it into balls, flattening it into pancakes, or creating intricate sculptures, each action reveals something unique about them. It could be their level of focus, their creativity, or even how they approach problem-solving.
Benefits include:
These are all important skills for children, especially as they prepare to move into formal education. The benefit of using clay is that it’s a natural, moldable medium that can be used as a cement, an adhesive and even a paint.
Paul R White, an American clinical social worker, has been using clay as a therapeutic tool for over 30 years. In his book, CLAYtherapy, he talks about how clay play can naturally facilitate meaningful conversations between children and adults. He developed numerous unique aids and techniques that have assisted him in teaching children to cope with stress, express feelings and to solve problems, including through the use and manipulation of clay. White also presented a paper on clay therapy to the World Congress of Child Play Therapy and Child Psychotherapy in London, England.
He has used clay in his practice as an ice breaker, as an aggression reliever and as a primary tool in treatment.
In his book, White says “Through mutual clay play, a conversation between child and counselor automatically emerges. Dialogue doesn’t have to be forced or fabricated, but happens naturally when the counselor is revealing, demonstrating and teaching this dynamic and engaging clay process and the child is asking, learning and experiencing his or her own trial and error. This manner of interaction links the adult with the child through a hands-on, verbal, nonintrusive, problem-solving counselling process.”
Lisa Terreni, a senior lecturer in early childhood education, also champions the use of clay. She believes it gives children another language for expressing their thoughts and ideas.
“From many anecdotal observations of children using clay I feel strongly that, apart from teaching young children the physical skills required to use the medium successfully to create three dimensional artworks, using clay gives children another language for expressing their thoughts, ideas and emerging working theories about their world,” she said in a blog post for Early Arts.
Marvin Bartel, a professor of art at Goshen College in the United States, says in a blog post on his website that ‘clay is so fascinating that some children work for long periods without any adult motivation to maintain their interest. It can be a great way to extend the attention span of some children.’

According to experts from Pennsylvania State University, children will show many parts of themselves through clay experiences:
One of the lesser-known but incredibly important benefits of clay play is muscle development. When children manipulate clay, they’re actually engaging both fine and large muscles, which is crucial for their physical development.

Anxiety
One study in Iran aimed to examine the impact of clay therapy and narrative therapy on reducing anxiety levels in pre-school children. The study involved 30 kindergarten children who were divided into three groups: 10 in the clay therapy group, 10 in the narrative therapy group, and 10 in the control group. The study found significant differences in anxiety levels among the groups. Both the clay therapy and narrative therapy groups showed a reduction in anxiety compared to the control group. The clay therapy group had a mean score of 3.63, and the narrative therapy group had a mean score of 2.83, both of which were significantly different from the control group’s mean score of -0.71. However, there was no significant difference between the clay therapy and narrative therapy groups in terms of anxiety reduction.
The study concludes that both clay and narrative therapies are effective in improving self-esteem, school performance, and sociability of the children, as reported by the parents.
Psychosocial Wellbeing
Another study out of Kenya, looked at how clay play supported children who lost access to schools during the pandemic, affecting children’s right to education and their psychosocial wellbeing.
The study, published in the East African Journal of Arts and Social Sciences, looked into the psychosocial effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on children and how play, particularly with painting and clay modelling, can be a therapeutic and educational tool. The paper argues that these forms of play can help children cope with the stresses and traumas induced by the pandemic, while also promoting cognitive and social learning.
The study argues that play with art forms like painting and clay modelling can be powerful tools for cognitive and social learning. They can also serve as therapeutic activities to counter depression and violent behaviour. Activities such as clay modelling and painting are described as non-serious activities that free the mind and are excellent for expression. Clay is described as a malleable material that can be easily manipulated, while painting offers a colourful medium for expression.
The study suggests that these art-based activities should be integrated into the curriculum, especially for children aged four to six, to enhance their psycho-motor and creativity development.
Fine Motor Skills
An Indonesian study investigated the impact of constructive play with clay on children’s fine motor skills. The small study by researchers from STKIP Kusuma Negara included two groups of 11 children each, one as the experimental group and the other as the control group. The study used test observation techniques for data collection and employs both descriptive and nonparametric statistical analysis. The results indicated a significant difference between the two groups, suggesting that constructive play with clay positively impacts children’s fine motor skills.
In the study, the authors highlight the physical aspects of working with clay.
“Working with clay fosters large muscle and fine motor control. Clay is fairly resistant and will need to be kneaded and worked to make it pliable. Children can stand or sit while using clay. Standing provides the advantage of a whole-body muscular reaction to the clay. Hard clay provides solid resistance the child must overcome. This will involve using the shoulders, arms, hands, and fingers. Playing with clay develops large muscles and fine motor control because the clay is quite resistant and kneaded to make it soft.”
The benefits of clay play in early childhood development are supported not only by expert opinions but also by a growing body of scientific research. From fostering creativity and social skills to enhancing both fine and large muscle development, clay play serves as a multifaceted educational tool.
References:
At Little Scholars School of Early Learning, we’re dedicated to shaping bright futures and instilling a lifelong passion for learning. With our strategically located childcare centres in Brisbane and the Gold Coast, we provide tailored educational experiences designed to foster your child’s holistic development.
Let us hold your hand and help looking for a child care centre. Leave your details with us and we’ll be in contact to arrange a time for a ‘Campus Tour’ and we will answer any questions you might have!
"*" indicates required fields
Let us hold your hand and help looking for a child care centre. Leave your details with us and we’ll be in contact to arrange a time for a ‘Campus Tour’ and we will answer any questions you might have!
"*" indicates required fields