The children, educators, staff and families are celebrating Little Scholars George Street receiving an Exceeding result in the National Quality Standards (NQS) Assessment and Rating recently.
Situated in the heart of Brisbane’s bustling central business district, Little Scholars George Street provides exceptional early learning and care for 108 children. Its unique location places children just steps away from some of Brisbane’s most iconic cultural spaces, including the Queensland State Library, Brisbane Square Library, Queensland Museum, and the Gallery of Modern Art.
Excursions like these, which pique children’s curiosity and understanding of the world, are just some of the unique offerings from Little Scholars George Street.
As Little Scholars approaches its 10th anniversary of serving South East Queensland families, the children, and the educators, are the heart of what makes this exceeding campus so special.
“Our team is incredibly dedicated to providing the best early education experience for our little scholars,” says Jae Fraser, founder of Little Scholars. “The Exceeding rating is a testament to their hard work, innovation, and commitment to the children’s development. They consistently go above and beyond to create a nurturing environment where each child can thrive, while also supporting families by making Little Scholars a true home away from home.”
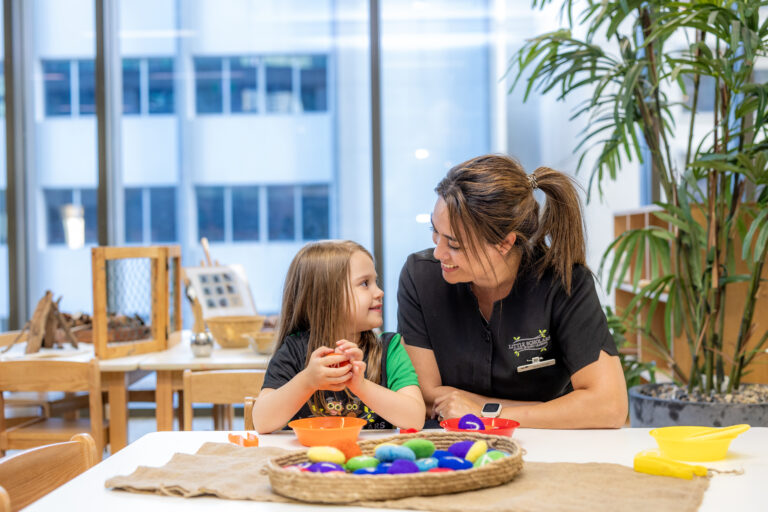

Little Scholars’ Collective Curriculum emphasises how much of its educational experiences are child led, and this was noted in George Street’s assessment.
“Educators and service leaders actively sought the perspectives, opinions, and voices of children, families, and the community,” the assessment noted.
The assessment went on to say the George Street team demonstrated a strong, ongoing commitment to meaningful, authentic, and regular engagement to inform the program.
It highlighted the collaboration Little Scholars has with families and the community supported educators in designing and implementing programs that promoted belonging, valued each person’s unique contribution, and created a sense of wellbeing and calm throughout the service.
George Street team demonstrated a strong, ongoing commitment to meaningful, authentic, and regular engagement to inform the program.
An example of this approach is the Children’s Council, a key initiative at all Little Scholars campuses, including George Street. The Council, composed of children, their early childhood teacher, and educational leader, meets monthly to gather feedback on the children’s kindergarten experience and empower them to participate in decisions affecting their campus. The child-led meetings occasionally veer off-topic, but they offer invaluable insights into the children’s interests and perspectives.
Understanding how busy its families are, Little Scholars George Street goes the extra mile to ease parents’ daily challenges. The campus offers free parking, rare in the heart of Brisbane, along with a valet service where a caring staff member greets children and escorts them to the campus.
Additional support offered to families includes a daily breakfast bar, take-away meals to simplify dinner time, and quarterly date nights, giving parents the opportunity to reconnect while their children enjoy an evening of fun with friends.
“Given our proximity to government departments, law firms, and entertainment venues, we know our parents have demanding schedules,” Jae explains. “That’s why we’re committed to providing these additional services that truly make a difference in their daily lives.”
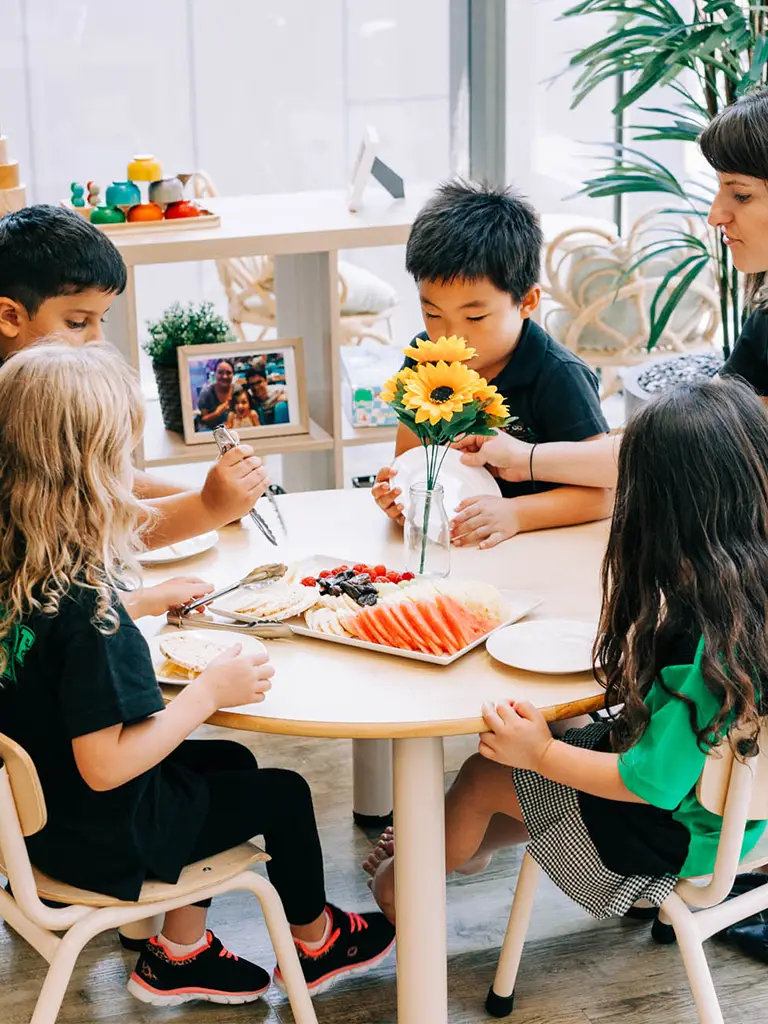

Amy Robertson, campus manager of Little Scholars George Street can barely contain her excitement, and says she’s proud of her staff, who she believes always goes above and beyond.
“Our recent assessment and rating at George Street has highlighted the exceptional quality of care and education our campus provides. We are proud to receive an exceeding rating, a testament to the dedication and professionalism of our educators,” says Amy.
“This achievement has been warmly received by our families, with one parent expressing, ‘We always knew the campus was exceeding, it’s gratifying to see the staff receive this well-deserved recognition from the Department,’” she adds.
Little Scholars George Street’s Exceeding rating reflects the hard work and dedication of its entire community, and it highlights the exceptional quality of early education and care provided at this remarkable campus.

While many Gold Coasters head to the southern suburbs on the weekend, the northern suburbs should not be overlooked for family-friendly weekend adventures! Starting in Stapylton and reaching to Pimpama, the most northerly suburbs of the Gold Coast also include Yatala, Alberton, Steiglitz, Gilberton, Norwell, Ormeau and Jacobs Well. Here you will find unique family activities, a range of family-friendly dining options, and some of the Gold Coast’s most unique play spaces. Here is your guide to getting the most out of a day in the Northern most parts of the Gold Coast.
South-east Queensland’s last original open-air Drive-In Cinema is located in Yatala, and boasts three massive screens accommodating up to 700 cars each night. Bring your camp chairs and sit out the back of your car to watch a movie, or bundle up the blankets, pillows and sleeping bags to make yourself comfortable in the back of your van, ute or car. Perfect for wriggly children, the privacy of sitting in your own vehicle means there is no need to worry if their bouncing around is bothering other cinema patrons. Movies screen every night of the week and they often host special event screenings too.
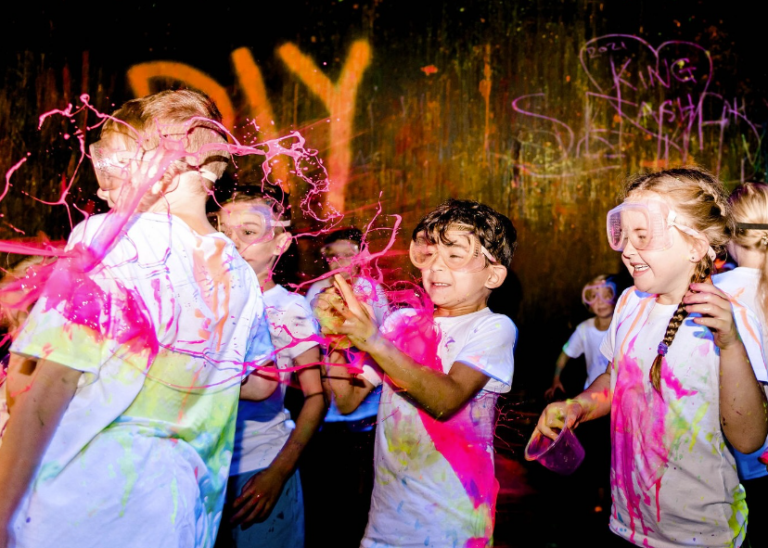
If your family is feeling creative, or looking to get messy, a workshop at DIY Invasion is sure to tick the box. Located at Staplyton, DIY Invasion run craft workshops ranging from resin art to painting, macrame and slime making – with their School Holiday Workshops always extremely popular for children. Another unique feature is their Splatter and Splash Room, which families can book for a private experience! Choose your own dance music, while letting your creativity run wild as you fling, flick, and splash paint around the room and over your fellow participants! This is a great space to unwind and tap into creativity.
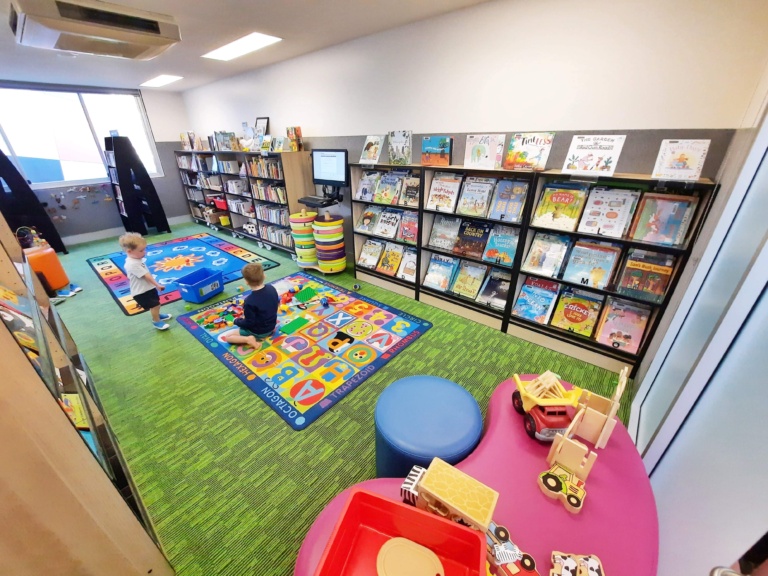

The only library located in the far northern suburbs, the Ormeau Community Lounge & Library is a hidden gem. Here you can visit the Gold Coast’s only Book Box corner, an early year’s library and play-based learning space delivered in partnership with Queensland State Library’s First 5 Forever program. Here children do not have to worry about being quiet, and they are actively encouraged to play with the many games and play resources available. Open six days a week, families can join in Story Time on Friday and Saturday mornings, or participate in Baby Rhyme Time and Toddler Time sessions during the week.
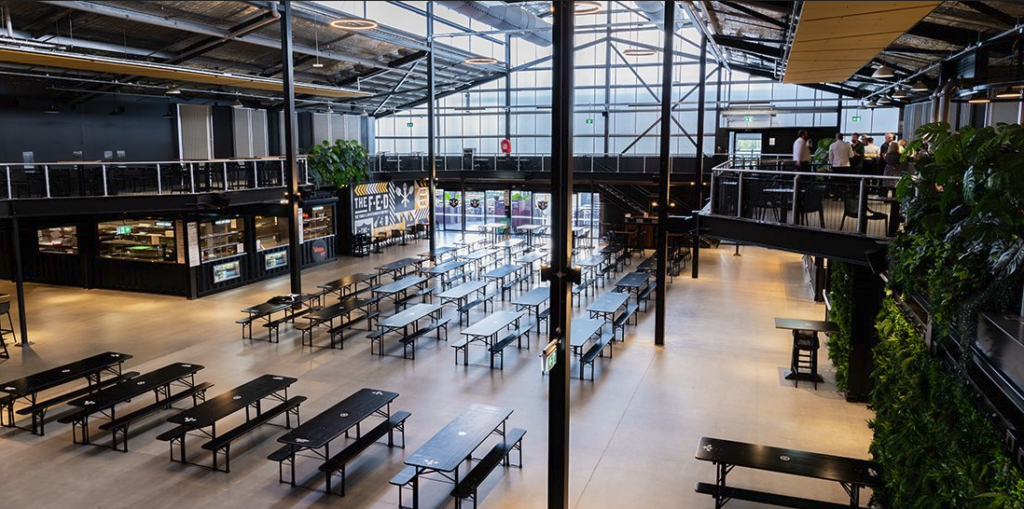

Distillery Road Market is a fresh and exciting new venue located in Eagleby, home to The F.E.D, a 2000-person food and entertainment space. Here you’ll find an expansive indoor/outdoor dining area, with a range of on-site eateries to choose from. Open Thursday – Sunday, the venue is family friendly with live music each evening and long beerhall-style tables to choose from. The best part is that diners can choose meals from six different food outlets, meaning that all tastes and dietary requirements can be catered for! The casual vibe of this venue is perfect for an early dinner with the family, where children and parents can relax, move around, dance and enjoy a great meal together.
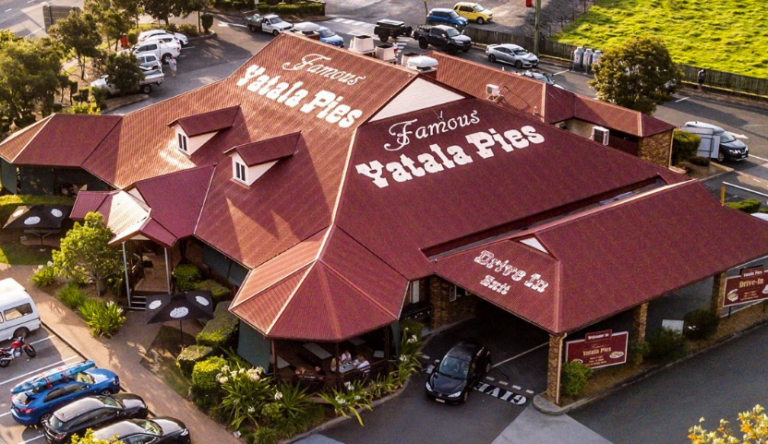

Yatala Pies has been a landmark in the Yatala area for more than 130 years, these days selling around 3,500 pies daily! Well known as a halfway stop on the journey between Brisbane and the Gold Coast, northern Gold Coast locals are lucky to have this icon right here in their backyard. Selling some of the best pies on the Gold Coast, the quality is exceptional and the range delicious. Choose from dine in or takeaway, you can grab a hot, ready-to-eat snack pie, or take-home, oven-ready family pies and snack pie packs. With something for everyone, the family will love a stop in at Yatala Pies any time of the day.
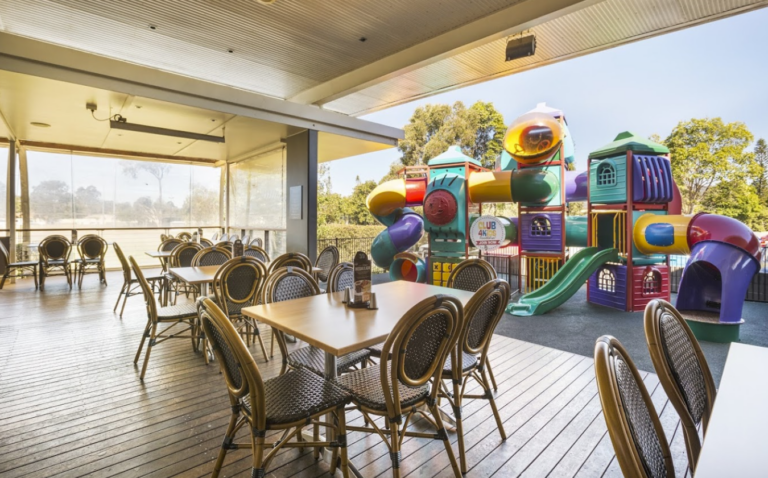

The Norfolk Tavern has got to be the most family-friendly dining option in the northern Gold Coast. Indoors you will find a bright and spacious dining room, while outside there is a wraparound veranda with ample space for dining, opening on to a huge children’s playground. The award-winning Bistro has menu options to suit every taste, from fresh seafood to steaks, pastas, salads and all the traditional pub fare. Extremely popular on weekends, be sure to book a spot on the deck if you are dining with children for easy line of sight from your table to the playground.
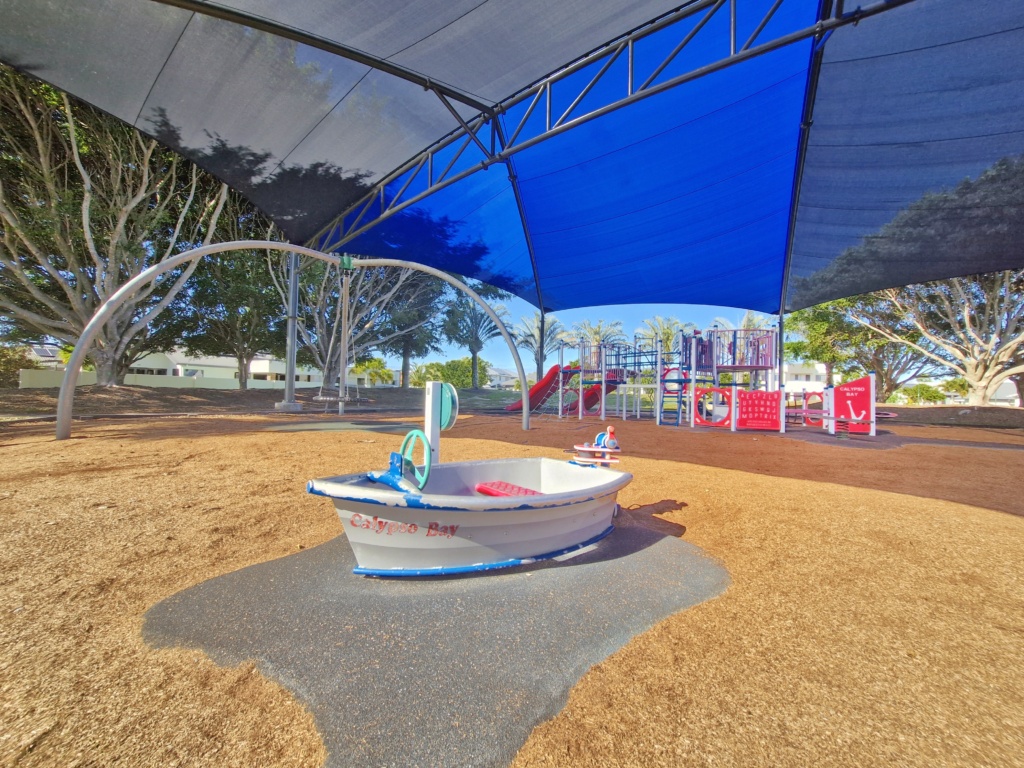

A nautical themed playground appropriate for its position by the water and close by the Calypso Bay Marina, here you’ll find a pirate ship brimming with bridges, wheels, slides and nets – be careful, you might even be asked to walk the plank! Underneath the pirate ship the imaginative play space is further extended, with a small shop counter set up, tunnel frames and other interactive game panels. The swing set with all abilities swing is always popular, as is the spinners and hammock swing. There’s also a little boat for children to pretend to fish or start the engine!

While many think the most northern beach area for children to swim is at Paradise Point, there is a lesser-known spot at the very northern edge of the Gold Coast – Lions Park at Jacobs Well. With easy access from the carpark, you are at a small, shaded beach in just a few steps. The swimming enclosure here has a small sandy beach, a large shade sail over the sand, and few waves, making it ideal for toddlers and younger children gaining confidence in the ocean. Parents will love the ability to sit on a blanket under the shade and still be close enough to their children in the water.
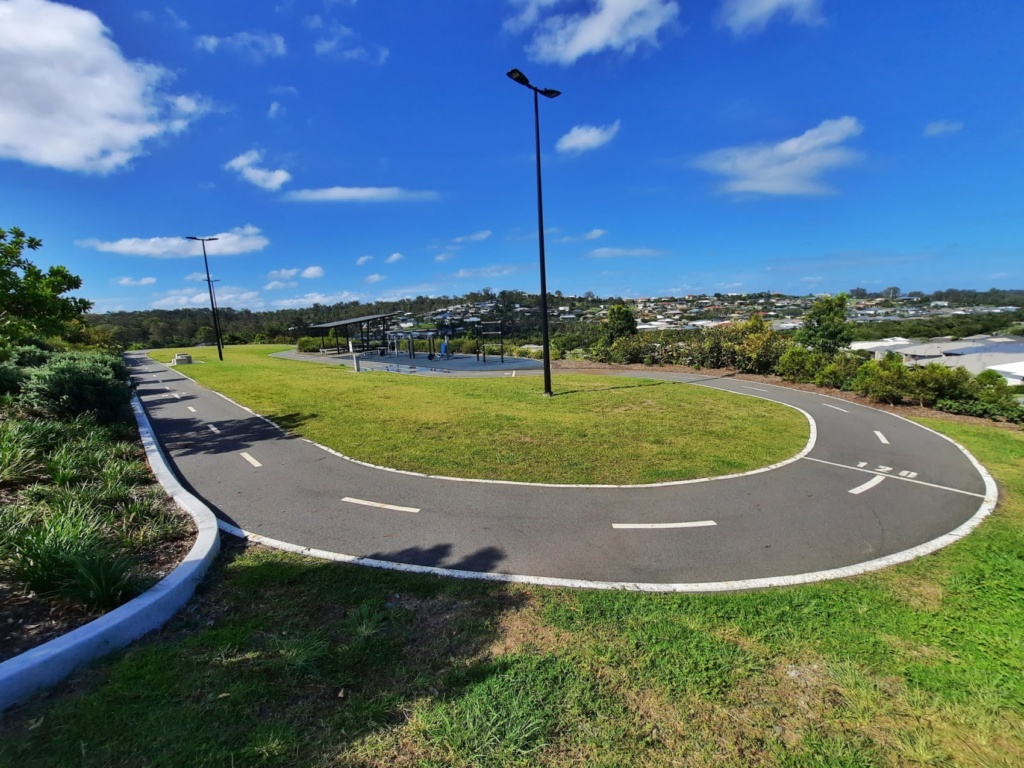

While the playground at Outlook Park, Ormeau may be tiny, pack the bicycles and prepare yourselves for the surprise bike tracks that make this a fabulous spot to visit! Set on a steep slope, Outlook Park is laid out over three levels. At the top you’ll find a small playground best suited for toddlers, and then on the middle and lower level there are two bike tracks, perfect for racing on. While the playground is very small, the bike tracks are great for bicycles, skateboards or scooters, and children will love lining up at the start line and racing the loops to the finish. Celebrate with some pretend play medal ceremonies on the dais at the track!
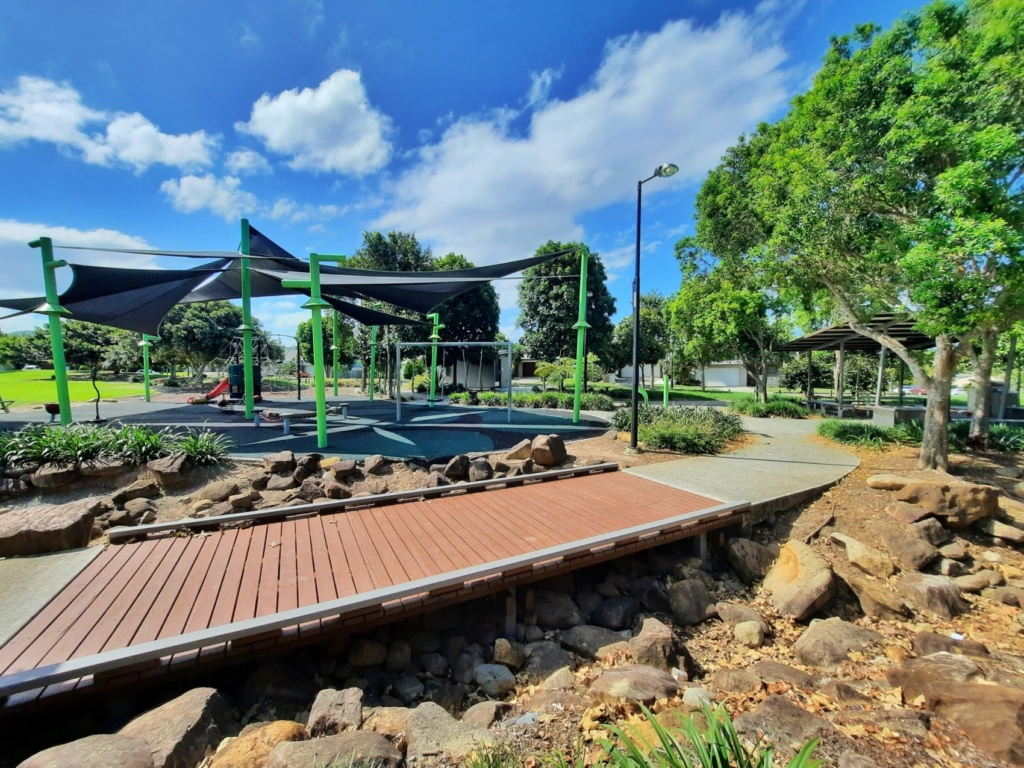

Hilltop Park in Ormeau is an older park, but still delivers a great time. Split into two sections, toddlers will love the smaller, shady play area with a car, climbing frame and mini playground with slide and swing. The main playground space is better suited for children over five, with a larger playground and slide, large climbing net, balance beams, spinners and swings. Children can also climb the ramp up to the old water tower, which has been converted into a play structure.
The northern Gold Coast offers a variety of unique and exciting activities for the whole family. From classic drive-in movies to hands-on creative workshops, scenic playgrounds, and delicious dining options, these suburbs have something for everyone. Whether you’re looking for a relaxing day by the water or a more adventurous outing, there’s no shortage of fun to be had. Next time you’re planning a family day out, consider exploring the hidden gems of Stapylton, Ormeau, Yatala, and beyond—you might just discover your new favourite weekend spot!
Little Scholars provides quality early education and care for children across South East Queensland, including five early learning campuses in Stapylton, Yatala and Ormeau.
We offer your child the very best facilities, resources and early educational, play-based programs available, which are underpinned by the early years learning framework. We believe that through quality education and care for children, we can also encourage, assist, and support the entire family.
Our dedicated team of educators are committed to the individual needs and interests of children and their families, and thus we encourage and welcome family input and involvement.
Find Lara’s recommendations at her website Mrs. Lardeedah.com, and follow her socials Facebook and Instagram
These days, life feels busier, more rushed, more overwhelming, so the need for bringing calm into our bodies and minds has never been more welcome.
We introduced our Little Scholars Mindfulness Program back in 2021, a time when the world was chaotic, and the early learning sector was facing its own unique challenges. While thankfully we’ve moved through that period and the world has adjusted, the importance of mindfulness, yoga, and meditation in early learning remains significant. These practices continue to play a crucial role in helping children develop focus, emotional resilience, and a sense of inner peace that supports their overall growth and wellbeing. But that’s not all these practices offer children.
We’ll share all the benefits mindfulness practices provide children, and we get to speak with Annette Hartland, a former Little Scholars educator who now teaches yoga and meditation full time to young children, including our little scholars.
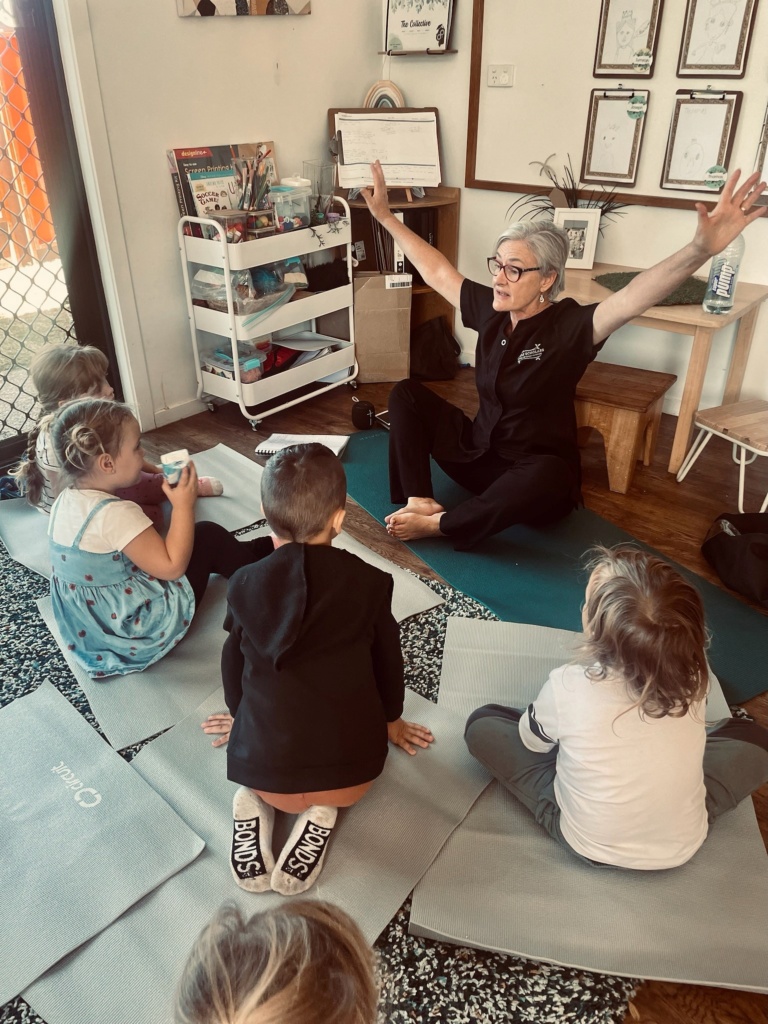

Annette once worked as an educator in our Ashmore campus, leaving to follow her passion of becoming a yoga instructor. However, achieving her dream meant she actually returned to us in a different capacity, she now leads yoga and meditation practice at several of our campuses and our support office.
We asked Annette how she got started practicing yoga, and what she saw as the benefits of mindfulness practices for children.
How did you get involved in yoga and what is it like to mix your passion for yoga with your great affection for young children?
It’s been so long that I don’t remember a time in my life when I haven’t practised some type of yoga/meditation. The short story is that my sister asked me to attend classes with her just after my second child was born. I’ve attended regularly ever since. My daughter’s almost 30 years old! Cliche as it sounds, Children are the future. They are inquisitive, flexible in mind and body and are ready to learn. It is vital to nurture this love of learning and develop a discipline of moving within their own space and taking time to be calm and think.
What are the emotional benefits of the practice?
Yoga and meditation practice take you inside yourself to be more aware of the movement of your breath, your body and your mind. We use the breath to be able to deal with situations calmly. One deep inhalation and a long exhalation remind us to pause to consider all the possibilities. Yoga teaches that all living beings are connected. This has a positive benefit for all living creatures. The children feel the difference between moving, being still and being relaxed.
What are the physical benefits?
Move it or lose it is the simplest answer. Children become aware of how much space they like at particular times eg. resting by themselves, partner poses, time to move with wide arms and stance or just a little space around their body. They develop concentration to maintain balance, they strengthen their muscles and become more flexible. We love moving rigorously and then freezing – the difference between effort and ease, mobile and relaxed.
What have you witnessed after teaching yoga with the children?
After teaching certain breathwork or postures, which I learned through the Zenergy yoga therapy course, the children settle more easily and are able to participate with more awareness. Some children are more aware of others and volunteer to be giving of themselves.
Do you have any advice for parents on bringing more mindfulness at home?
Take the time to be present to your children for a while each day, at least 10 minutes. No TV or telephones or music – just you and your child. Take a walk in nature, gaze at the stars, sit with a pet, cuddle on the couch and chat or be silent or breathe together. Listen, smell, taste, touch, feel … connect. This makes precious memories with your children.
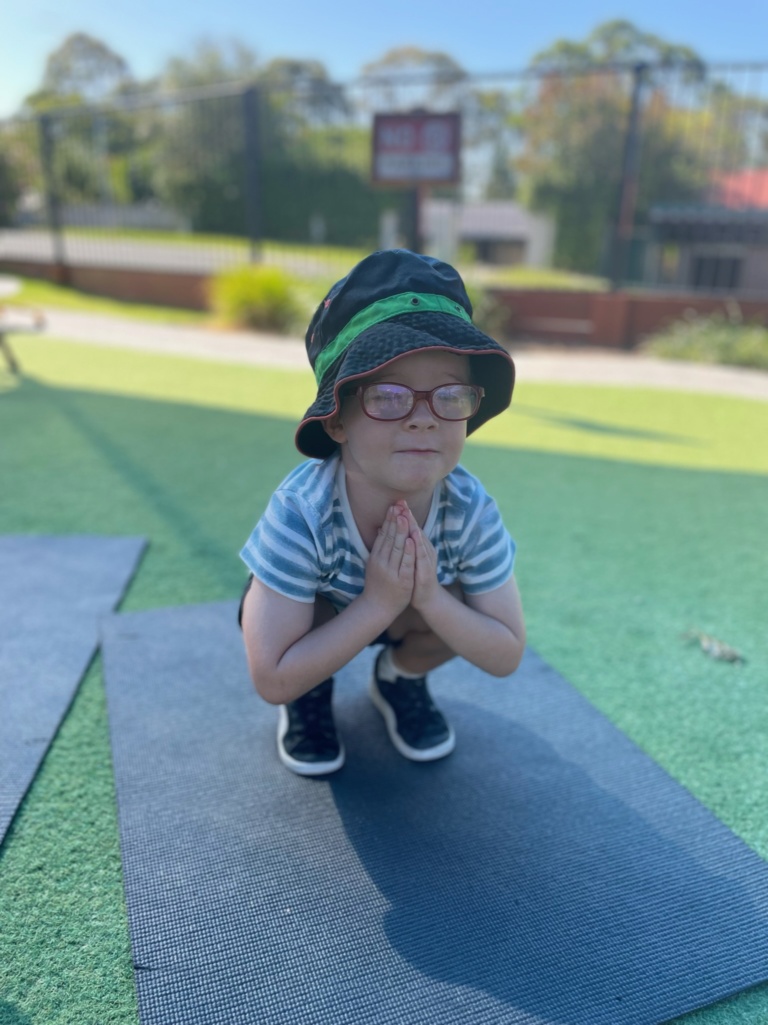

As mentioned, one facet of our mindfulness program is offering our little scholars yoga sessions delivered by experts like Annette, and as she says, yoga offers a multitude of benefits for emotional and physical development, backed by research.
On the physical side, yoga enhances flexibility, coordination, balance, and posture. Yoga requires our full attention, requiring us to focus on the present and be fully aware of what our body is doing at any one time. It also helps develop fine and gross motor skills, guiding us to learn to control breathing, our stance and where we’re putting our weight, and flowing through to the next posture.
On the emotional side, by focusing on movement, balance, breathing and everything else that yoga requires of us means that we’re fully present in the moment, practicing self-awareness and mindfulness, reducing stress and any outside ‘noise’, promoting relaxation, bringing a sense of calm and wellbeing. In turn, this means we’re developing emotional regulation and resilience.
For children who are just learning how to interpret and manage their emotions, this is a fantastic way for them to deal with life’s challenges big and small.
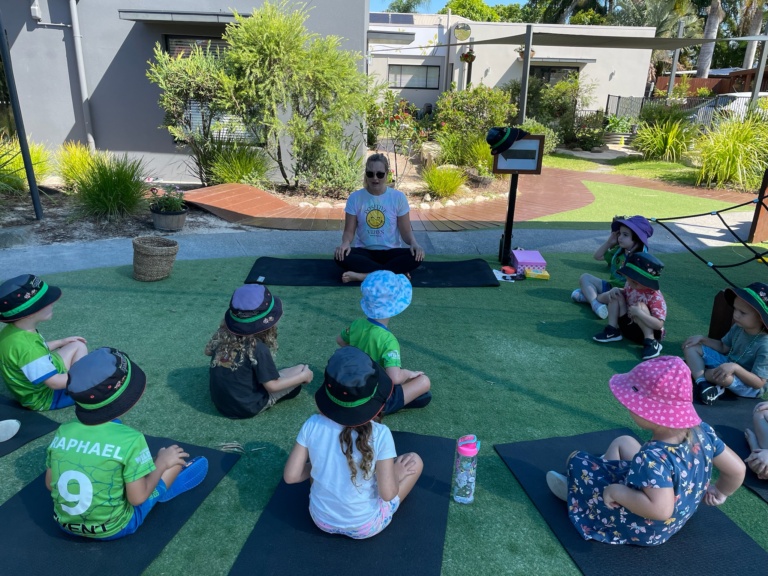

Another and even easier way to bring more mindfulness to our day-to-day that anyone, including children, can do is practice breathing techniques to calm the mind and body. Here are some of our favourite breathing techniques for children.
1. Ask children to lie on the floor and place a small object, such as a soft toy or bean bag on their belly. Get them to place their hands by their side and breathe normally, watching the object go up and down. You could count as they inhale and exhale ‘breathe in 1, 2, 3, breathe out 1,2,3.’
2. Print or cut out some square, rectangle or triangle shapes and give one to each child. Ask the children to trace their finger around the shape, breathing in while moving their finger along one edge of the shape, hold their breath for a few seconds before breathing out, while tracing around the next side of the shape. Repeat this a number of times.
Children can also use their own hand as the shape, using a finger on the other hand to trace up the side of a finger while breathing in and down the other side of the finger while breathing out, before moving on the next finger.
3. While sitting comfortably, model for the children how to create a circle shape with their hands and ask them to imagine that inside the circle is a mug of hot chocolate. Ask the children to breathe in slowly to smell the hot chocolate, and then blow out slowly to cool it down, repeating this a number of times.
Yoga for Children and Young People’s Mental Health and Well-Being: Research Review and Reflections on the Mental Health Potentials of Yoga: Ingunn Hagen and Usha S. Nayar, Department of Psychology, Norwegian University of Science and Technology, NTNU, Trondheim, Norway New School University, New York, USA
The effects of yoga on mental health in school-aged children: A Systematic Review and Narrative Synthesis of Randomised Control Trials, Kirti Khunti, Sadie Boniface, Emma Norris, Cesar M De Oliveira, and Nicola Shelton, University College London (UCL), London, UK, Kings College London, London, UK,
Brunel University, London, UK
Scoping Review of Yoga in Schools: Mental Health and Cognitive Outcomes in Both Neurotypical and Neurodiverse Youth Populations, Niamh Hart, Samantha Fawkner, Ailsa Niven, Josie N Booth, University of Edinburgh

The Gold Coast is known for its abundance of good food and stunning dining options, but when you have young children in tow – often the thought of dining out can be daunting. Thankfully, many local restauranteurs have heard the call of parents seeking family-friendly dining options. We’re now seeing dining venues with amazing menus, family-friendly fit outs and features to help keep the children occupied while you enjoy a hot meal. Whether it be a playground, a simple children’s corner, or open spaces to move around safely, there are plenty of choices for you to enjoy your next meal out. Here are my top six family-friendly dining venues on the Gold Coast that you should be sure to visit!
This shopping centre café is a hidden gem, saving the sanity of parents for many years now. With opening hours stretching from 5.30am – 9pm, you can often find those parents with early-risers enjoying a hot coffee at Café 63 in the early hours. Located in the incredible “Backyard” precinct at Westfield Coomera, the outdoor dining area overlooks a fun-filled obstacle course with adventure play suited to four-eight year olds. For the youngest children, a nearby splash pad and toddler sensory zone also serve as great spaces to stretch the legs while waiting for your meals to be served. The menu here is extensive and well-priced, including a fabulous children’s menu that will please everyone.
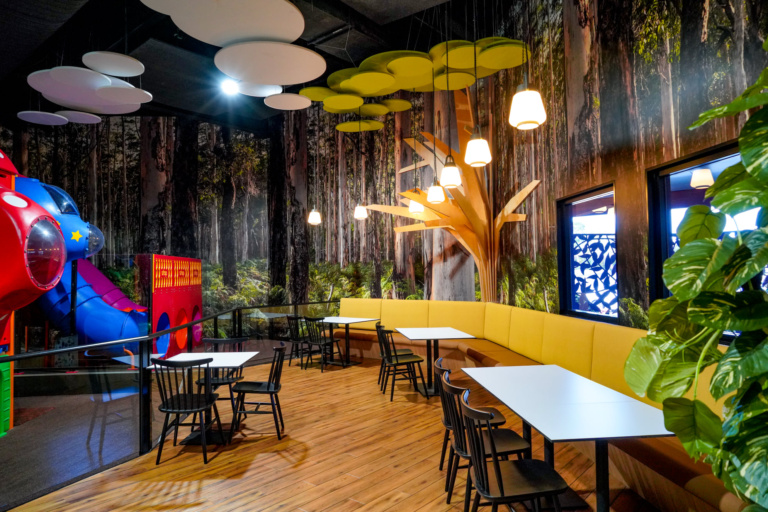

Here you will find a huge indoor children’s playground for four-12 year olds, with a family specific dining space attached. Separate from the rest of The Wattle Hotel’s restaurant, this glassed-off dining room overlooks the playground and contains about 15 tables. Here children can easily move back and forth between the playground and the table while their parents can see them at all times. There is a great children’s menu and delicious daily specials to enjoy, this is modern bistro dining that can be enjoyed by all the family.

A café best known amongst the Coast’s cyclists thanks to its location near the Velodrome and bike shops, Cadence Café also caters beautifully to families seeking great food. Set across three terraced levels, the venue is connected by a central path and steps – at the top is the café, the middle level has plenty of dining tables and chairs, and the lower level is home to high bar tables overlooking a fenced children’s play space. All levels are shaded by a beautiful fig tree, have ramp access, and dogs are also welcome in the outdoor areas. Serving breakfast and lunch, the menu caters well to families, and you are sure to enjoy a delicious meal.
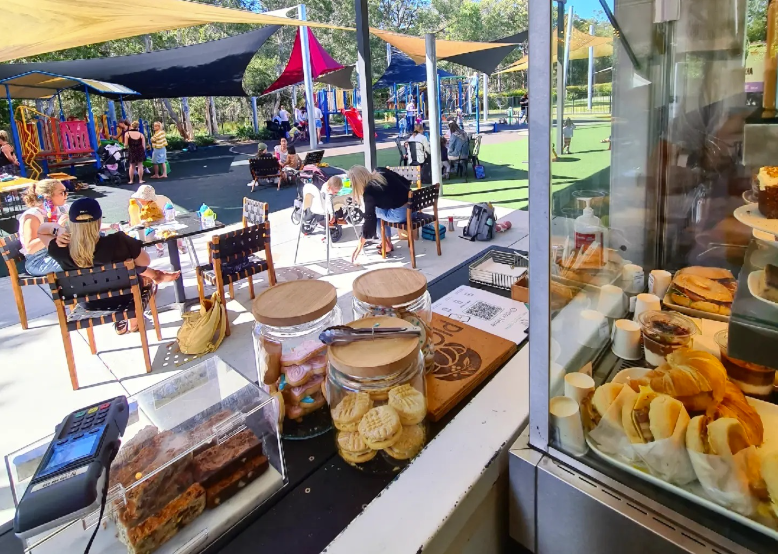

Just off the hustle and bustle of Olsen Avenue sits the Latte Lounge, a family-friendly oasis amongst the gum trees. Here you will find house-roasted specialty coffee and a delectable brunch menu, plus one of the best children’s menus you will find at a café. The open-air café is almost the second-best attraction, when you see the large, easily accessible playground right in the middle of the café. Designed for all ages, this fenced café and playground is covered by large shade sails and offers plenty of shady spots to enjoy your meal. With its central Gold Coast location, this is also an extremely popular spot for birthday parties and play dates. Thankfully, due to the size of the café and playground it never feels overly busy or crowded and is always a delightful outing.
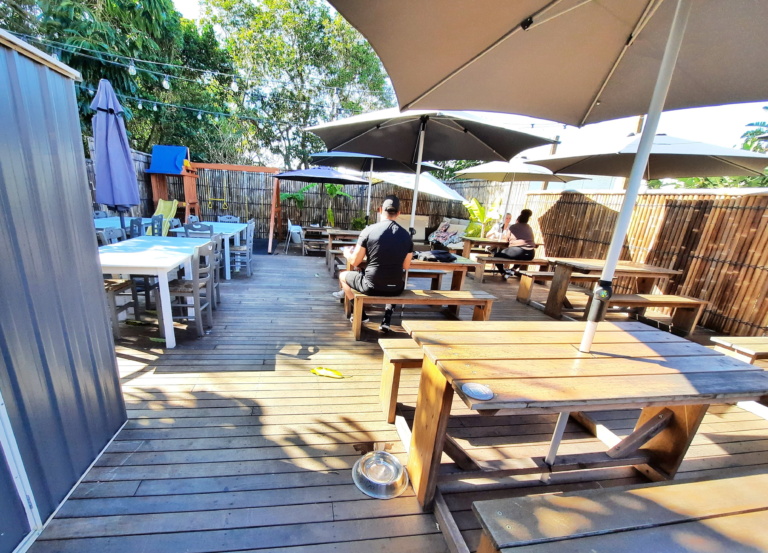

This hidden gem on the southern end at first appears to be a juice bar, but venture inside and you will find a breezy indoor/outdoor café with children’s playground! Popular with the locals, this unassuming little spot is filled with sunshine, great food and service with a smile. This is a family-run café with its roots in healthy superfoods that taste phenomenal. Dog friendly, the outdoor deck is the place to be, with easy line of site to the children’s playground. The café kitchen is only open Thursday – Monday, but the juice and smoothie bar is open 7 days.
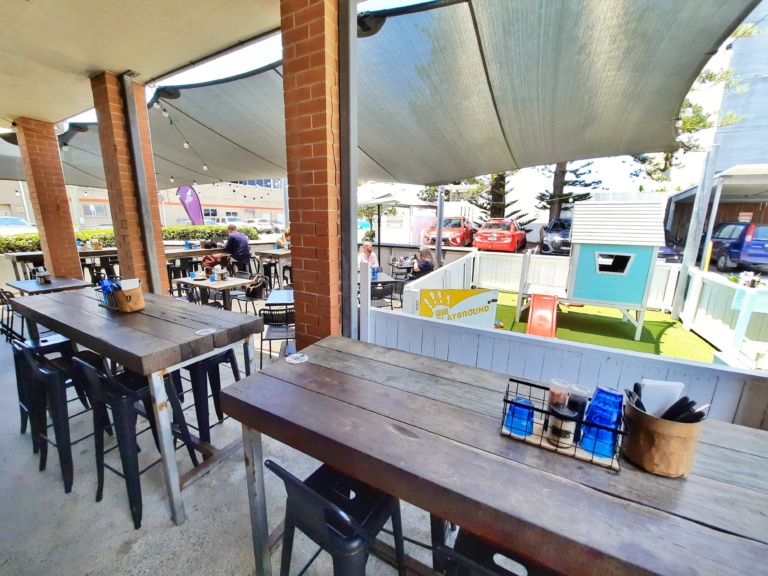

With beautiful coastal vibes, indoor/outdoor dining is essential on the Gold Coast, and BSKT serves it up perfectly. Located just steps away from the beach, BSKT has delicious food, ample seating and a fenced children’s play area. Pronounced biscuit, this menu is packed with vibrant colours and bold flavours, but also caters well to children. BSKT doesn’t take books and this spot is extremely popular on the weekend, but wait times are usually short. Be sure to grab a spot outside under the patio to have easy access to the play area! Why not pack the swimwear and walk over to the beach afterwards!
Find Lara’s recommendations at her website Mrs. Lardeedah.com, and follow her socials Facebook and Instagram
Children’s positive views of themselves as learners are more important than being told they are clever.
This insight from Nathan Wallis’s talk at the Australian Childcare Alliance (ACA) conference resonated with us, and we believe it’s valuable for parents to hear. Our intention isn’t to make parents feel guilty for praising their children’s intelligence. We understand that parents aim to foster a strong sense of self and ability in their children, and we fully support this. However, Wallis emphasises that before the age of seven, children don’t need to prove their intelligence. Instead, they need to develop learning skills through play and believe in their ability to learn. According to Wallis, more play and less structured learning before age seven leads to better outcomes in adulthood.
“To put it simply, before seven, it doesn’t matter how clever your child is. What matters is how clever your child feels and their disposition towards themselves as learners,” Wallis, an educator who focuses on neuroscience, explained on the Future Focus podcast.
“You’re better off having a six-year-old who can only count to 20 but thinks they’re a good learner than a six-year-old who can count to 100 but doubts their cleverness.”
Wallis highlights that free play boosts creativity and problem-solving, which are essential for intelligence. Letting children freely build, create, and explore supports flexible thinking and a positive learning mindset.
At the conference, which attracted hundreds of early childhood educators, Wallis offered advice on how to support children in their confidence and ability to learn:
Experts at Early Childhood Australia agree that children learn about themselves, others, and the world around them through play.
“If you provide your child with plenty of opportunities for playing, exploring, discovering their interests, solving problems, and tackling challenges, then you’ll be laying a strong foundation for building self-confidence,” says David Lyons, CEO of Nido Early School, in a post on ECA’s The Spoke blog.
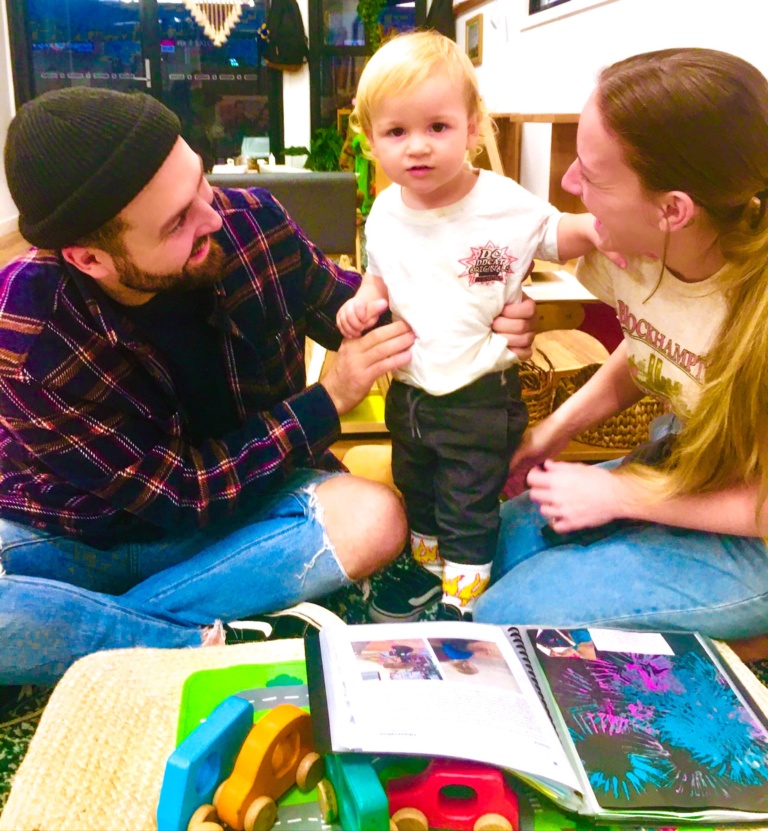

According to Be You, the national mental health and wellbeing initiative for learning communities in Australia, praise is most effective when adults are mindful of how and when they use it.
When praising children, Be You suggests focusing on their efforts and achievements.
“Praise that’s specific and acknowledges the process of completing an activity or solving a problem helps develop children’s learning and motivation. For example, you might say, ‘You put away your toys so nicely,’ ‘I noticed you were really trying hard at building that block tower,’ or ‘You’ve used so many bright colours in your painting.’ Children can then use this learning when they have similar experiences in the future.”
Lyons agrees and cautions against overpraising.
“Children need to discover and learn those things that give them personal enjoyment and fulfilment, not just do things to please their parents. Similarly, comparing a child to others can be detrimental to their confidence and self-esteem.”
Dealing with disappointment is also crucial for developing confidence.
“Everyone fails to achieve their goals sometimes – and this isn’t a bad thing. You can build children’s ability to deal with challenges by responding sympathetically and with encouragement, helping children focus on what they can change, and challenging ‘I can’t’ thinking by showing and saying you believe in them and reminding them of their achievements,” says Be You.
Wallis reinforces that play enables children to develop social, cognitive, and emotional skills through their own interests and in creative and innovative ways.
“Play-based learning teaches creativity, which is fundamental to growing intelligence and the ability to problem-solve. When children can take their time and make multiple attempts before achieving success, they build resilience and other important skills needed later in life,” says Wallis.
Supporting children in developing a positive self-view as learners is crucial, especially in their early years. Emphasising the importance of play over structured learning fosters creativity, problem-solving, and resilience. By providing nurturing relationships, paying attention to their efforts, and creating flexible learning environments, we can help children build the confidence they need to thrive.
As Nathan Wallis and other experts highlight, the goal is to make children feel capable and enthusiastic about learning. This foundation will benefit them not only in school but throughout their lives. At Little Scholars, we encourage our little ones to play, explore, and believe in themselves – because how they see themselves as learners today will shape their success tomorrow.
Over the past couple of months, we have started to launch woodworking stations at our campuses! But why, you may ask. It’s dangerous! They could get hurt! At Little Scholars, we actively guide children through ‘risky’ activities to build up their skills, confidence, and resilience. Engaging in woodworking helps children learn to assess and manage risks, develop fine motor skills, and boost their creativity and problem-solving abilities. By introducing these activities in a controlled and supervised environment, we ensure they gain valuable life skills while staying safe.
Woodworking is an excellent way for children to exercise their creative, practical and critical thinking skills. It allows them to express their ideas and figure out solutions to their projects.
As they measure, cut, and assemble pieces of wood, they enhance their hand-eye coordination and fine motor skills. These activities require precision and control, which are crucial for writing, drawing, and other tasks. Furthermore, using tools like hammers, saws, and sandpaper teaches them how to handle and manipulate objects with care and accuracy.
Guiding children through woodworking activities helps build their confidence and resilience. Completing a woodworking project, no matter how simple, gives children a sense of accomplishment and boosts their self-esteem. They learn that they can create something tangible and useful with their own hands. Additionally, the process often involves overcoming challenges and solving problems, which teaches persistence and resilience. These qualities are essential for tackling academic challenges and life’s obstacles.

Our little scholars begin their woodworking projects by making a plan. This may look like drawing out their project, or making a model out of cardboard or building blocks, discussing with their friends and educators what they’d like to build, how they’d like it to look, what tools they need in order to make their design come to life, and figure out any risks there may be and how to reduce chances of hurting themselves.
Introducing woodworking in a controlled environment allows children to learn about risk management. They are taught how to use tools safely, understand the potential dangers, and take appropriate precautions. This hands-on experience with ‘risky’ activities helps them develop a healthy respect for safety and risk assessment. They learn to think ahead, plan their actions, and make informed decisions to minimise risks, which are valuable skills both in and out of the workshop.
Some of their documented conversations with educators have included:
How can we make sure we are safe when using the tool table?
“You have to wear safety glasses.”
“If you step on a nail you can hurt your feet.”
“It can’t be too busy, I might knock something over or into someone and hurt them.”
What do you do at the tool table?
“I can measure the wood.”
“When I’m at the table I use the screwdriver.”
“I use nails to put in the wood.”
How does it make you feel when you build at the tool table?
“I like tools because I can screw something in.”
“I feel happy because I can make something.”

Woodworking supports creativity and problem-solving skills. As children design and build their projects, they must think creatively to overcome design challenges and find solutions. This process encourages them to experiment, explore new ideas, and think outside the box. The ability to approach problems creatively and develop innovative solutions is a real skill in today’s world, where adaptability and innovation are highly valued.
In addition to the practical skills, woodworking integrates educational concepts such as maths and science. Measuring pieces of wood, calculating dimensions, and understanding geometric shapes are all part of the woodworking process. Children also learn about the properties of different materials and the principles of mechanics and engineering. This hands-on application of academic subjects helps to reinforce their learning and makes these concepts more tangible and understandable.
By providing children with the opportunity to engage in woodworking, we are equipping them with a wide range of skills and experiences that will benefit them throughout their lives. Through careful supervision and guidance, we ensure that they can enjoy the benefits of this fun activity safely.
At Little Scholars, we have four pillars that underpin everything that we do at Little Scholars – for our children, families, educators, and our community.
As part of our annual awards, we have four awards dedicated to those Little Scholars’ values – learn, grow, inspire and contribute. This year, while our award-winning educators certainly personify all four pillars, but with their unique special skills and achievements, we’ve declared one clear winner for each pillar.
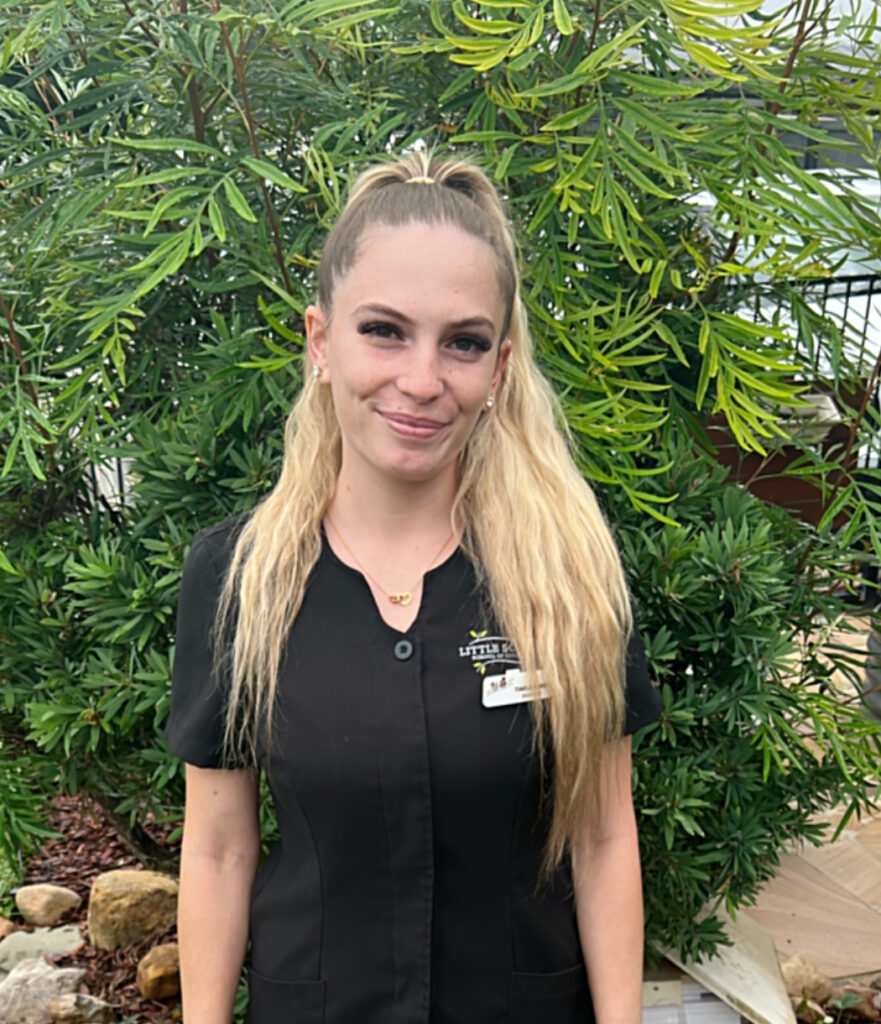

Tiahla at our Ashmore campus was named winner of the Pillar Award in the Learn category because she stepped up to become a lead educator, and she is happy to keep learning from her peers and further her education in the sector.
How long have you been an educator?
Four years
What made you pursue a career in early childhood education?
I feel like it was supposed to be as it all fell into place. I just came out of a casual job seeking for a new career journey and a job at Little Scholars Ashmore popped up. I applied for it and received the role the exact same day.
What’s the most rewarding and most challenging parts of your role? Watching their personalities blossom from a very young age, celebrating their personal developmental milestones with the children and building amazing relationships with families.
The most challenging part would be watching the children you have taught over the years move on to big school. We miss them so much!
What does winning this award mean to you?
Winning my award has meant the world to me, it makes me feel as though my progression and my achievements as an educator are noticed and valued.
Tahlia’s nomination
“Tiahla is always putting her hand up to learn new skills,” says Elise, campus manager for Little Scholars Ashmore.
“She is eager to grow from her peers, and will ask for help and support to build on her knowledge as an educator.”
Tiahla finished her Cert III and was keen to study her Diploma right away, Elise says.
“Tiahla has a bright future as an early childhood educator, as she values the importance of professional and personal growth through learning and collaborative partnerships.”
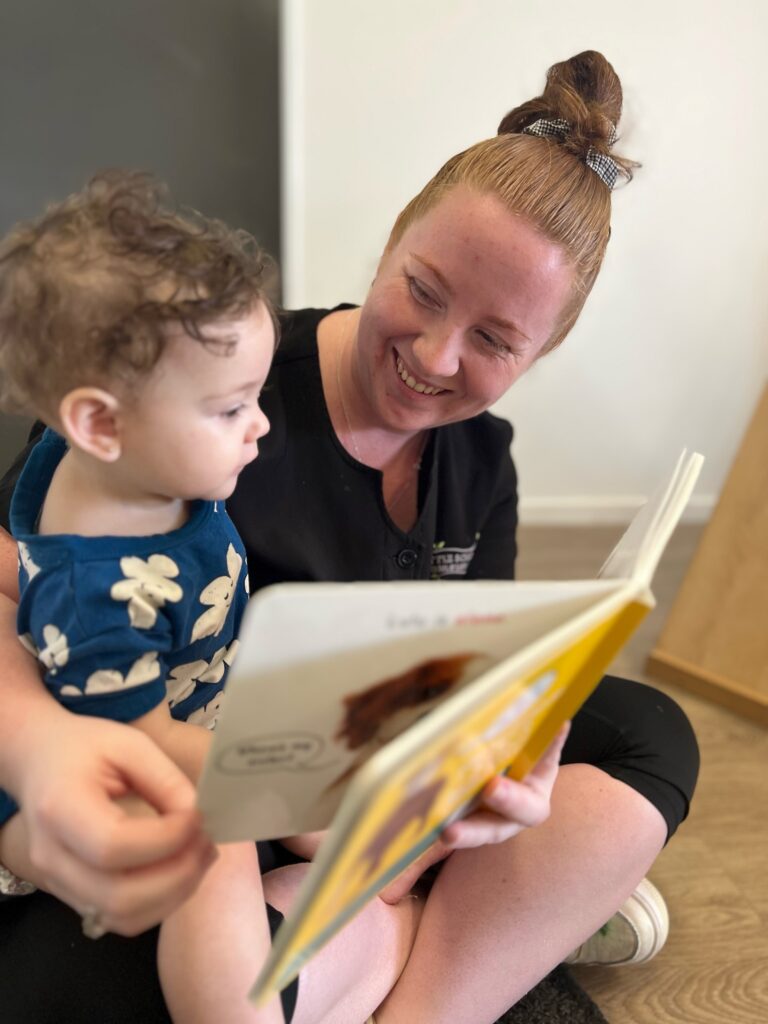

Keeva is an educator at Little Scholars Redland Bay South and is the recipient of an Inspire Little Scholars Pillar Award 2024.
How long have you been an educator, Keeva?
I have been an educator since 2016, so eight years now and have been with Little Scholars Redland Bay South since January 2023.
What made you pursue a career in early childhood education?
When I first started in early childhood education, I was studying an accounting degree, I quickly came to realise that I wanted to focus on my early childhood career. I fell in love with the children, how incredible they are and how much they could teach me. It wasn’t just the children that I fell in love with but also the challenges and limitless knowledge I could acquire and learn from to be the best educator possible.
What’s the most rewarding and most challenging parts of your role?
The most challenging part of my role is that I want to spend as much time as possible with each individual child everyday teaching them and learning from them but there is not always enough time. The most rewarding part of my job is watching the children hit all their goals and the excitement they display when they see us or accomplish goal. Mentoring and supporting other educators and seeing how far they have come in their journey is another rewarding aspect always leaving me feeling proud of their accomplishments.
What does winning this award mean to you? I was so shocked to receive this award, as I just turn up to work each day to do my best to support and guide both the children and educators. It felt so good to know that what I do each day is being noticed. It definitely makes you feel like you are doing a great job. To be recognised for the support and guidance I provide was so special and my heart felt full of love for my team. To me it cemented the fact that I am becoming the educator I always wanted to be
Keeva’s nomination
In Keeva’s nomination from Redland Bay South campus, it said, “Keeva is an educator who truly embodies each of the little scholars core pillars.
However, it is Keeva’s ability to inspire those around her, that is one of the most outstanding qualities. Keeva invests in mentoring those around her, inspiring their abilities to grow as educators utilising her existing knowledge and ability to learn more through professional development, to inspire each person to grow to full potential.”
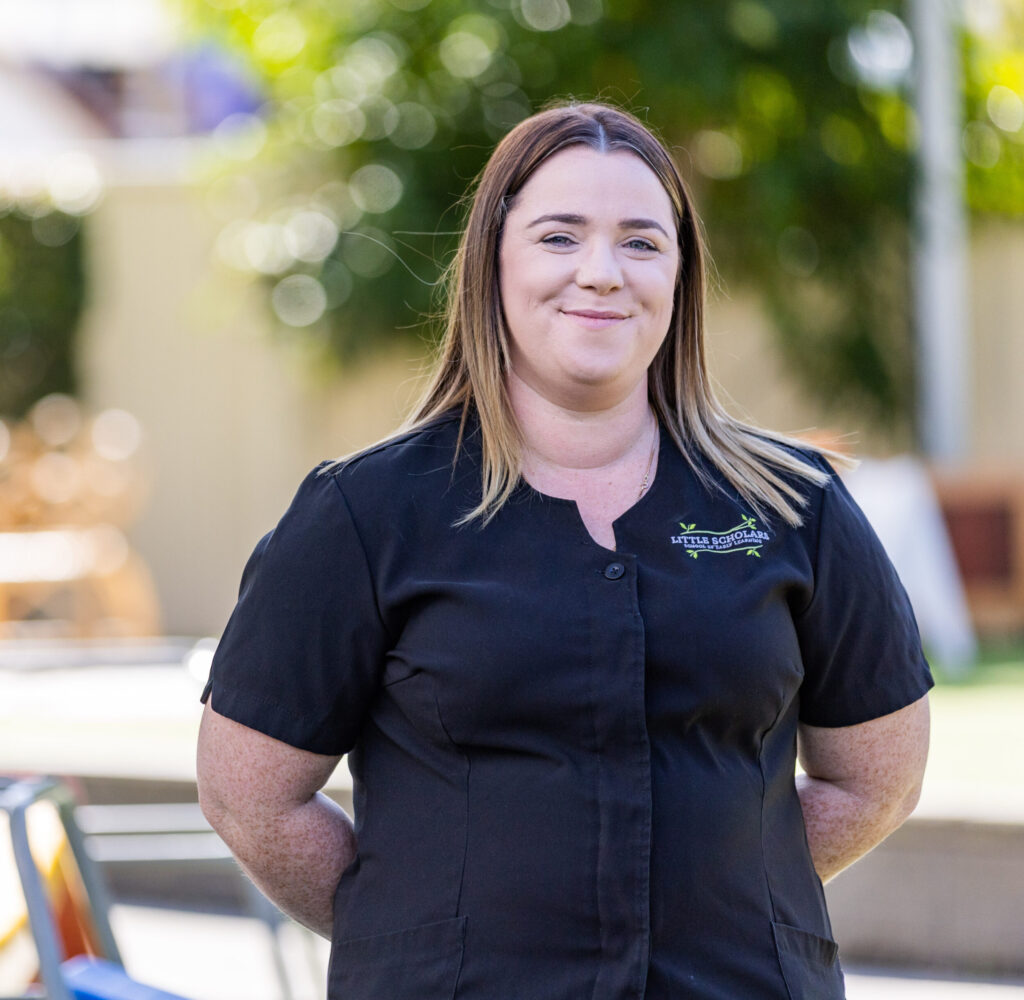

Claire is the educational leader at Little Scholars Nerang campus and has been awarded the 2024 Contribute pillar award.
How long have you been an educator and how long with Little Scholars?
I have been an early childhood educator for 18 years and with Little Scholars for nearly six years.
What made you pursue a career in early childhood education?
I’m not quite sure when I decided this was the path I wanted to take as I feel like it’s been my career goal since I was little. I still remember the way one of my kindergarten teachers, Miss Anderson, made me feel. She was fun, caring, and knowledgeable. I wanted to be that for someone and help children to learn in their own time and style. I liked the idea of being able to help shape the minds of little ones and set them up to be kind, respectful humans.
What are the most rewarding and most challenging parts of your role?
As educational leader within my campus, the most rewarding part of my role is watching both the children and educators flourish and grow as humans. It fills me with so much pride to watch the children reach their milestones and celebrate their successes with them as much as it does when educators gain new skills that help them in their professional career.
My biggest challenge is saying goodbye to the children as they venture off on their next journey into formal schooling. It happens each year but never gets easier to see them go after watching them grow and develop over the years.
What does winning this award mean to you?
Winning this award makes me feel like I am on the right path to creating what I hoped to. It reinforced the fact that I am in the right career and doing the right things to help create a better future and bring our campus closer to our local communities. I feel so proud to be recognised as the 2024 contribute pillar winner.
Claire’s nomination
Renee, campus manager, said, “Claire has remarkable attributes and will contribute to anything and everything you can throw at her.
She is passionate about supporting others and always willing to participate in any type of event, including her own professional growth.
Claire is dedicated within our Little Scholars family and her years with us is another wonderful example of her contribution to our sector.”
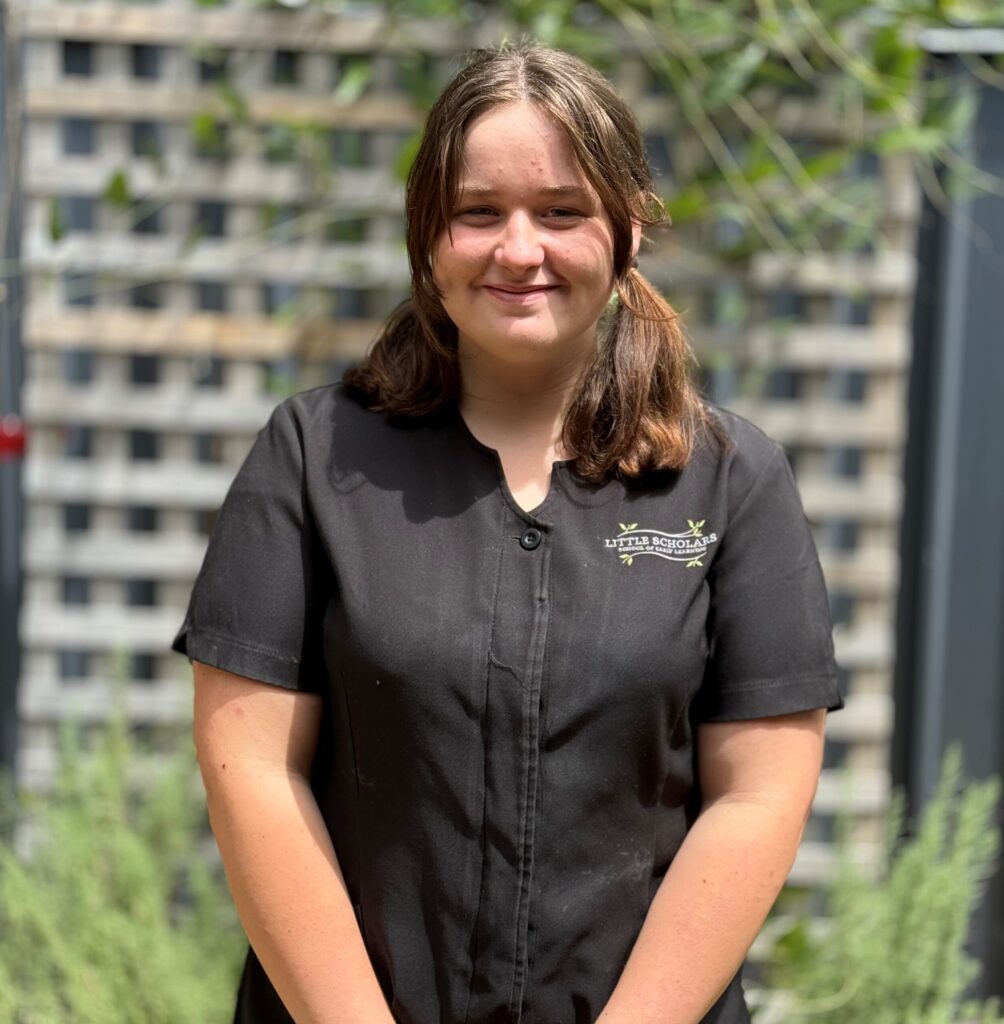

Stefenie, an educator at our Yatala campus, has remarkable attributes and we’re told her growth as an educator has been propelled by her enthusiasm to contribute, learn and inspire her team and go above and beyond not only for children, but families as well.
How long have you been an educator and with Little Scholars?
I have been an educator with Little Scholars for three years.
When you started, what was it about the role that made you want to stay in the sector?
When I was completing my work experience at the Yatala campus, I loved the relationships I was building with the children and I could see the impact educators had on the children.
What’s the most rewarding and most challenging parts of your role? The most rewarding part of my role is building such strong relationships with the children. The most challenging part is because I am so use to the younger age group, when I’m with the older children, I have to adjust my teaching style and interactions to their age groups.
What did being recognised for the Grow award mean to you?
It was really special because it really made me see how far I’ve come since being a 16 year old school based trainee. My confidence with the children and families, as well as my knowledge on child development has strengthened so much. I am a completely different educator and the fact that my leadership team can see and recognise it, it is a very special feeling.
Stef’s nomination
Stef at our Yatala campus was named winner of the Pillar Award in the Grow category because she’s grown from a trainee at the campus just a few years ago to now full time educator.
Sasha, campus manager at Little Scholars Yatala had this to say:
“Stef! What a superstar you are, and what a year you have had! From completing your Cert III as a school based trainee to jumping straight into full time work with us and then to go straight to studying your Diploma, nothing can stop you from achieving your goals, and we are so proud of how far you have come and the growth that you have achieved.”
For anyone who’s ever tried to learn a new language, you can probably attest to the fact it’s challenging. You think in one language and translate into another. There are new tenses, jargon, sentence structures, plurals versus singular words, never mind having the muscular movement necessary to form words with your mouth, the confidence to speak – we could go on and on. Now imagine what it could be like for a baby or small toddler?
There are benefits of course for children learning their mother tongue, or even a second language compared to adults learning language. According to German researchers, the melody of newborn babies’ cries is shaped by the sounds of their native language, which they hear in utero. Babies even babble in their first language. Wait, what? Meaning, from a very young age, they start copying the sounds and rhythms of the language they hear around them. This means they begin to use the same ups and downs in their voice (intonation) and the same timing as the language spoken at home. Plus, when babies babble, they often use the most common sounds (like consonants and vowels) from their family’s language. As babies continue to develop, their babbling starts to sound more like conversation, referred to as jargon, with a rhythm and tone resembling adult speech.
Fascinating, isn’t it?
So, how can you help your baby learn to speak? First, remember babies all develop at different ages and stages, so while some of their peers may be speaking, others may be more focused on movement, fine motor skills or something completely different.
Babies learn to communicate by listening to the people around them, especially their parents. They will:
Chatting with your baby is important, and it’s even better when it’s just the two of you. When it’s just parent and baby, without other adults or children around, baby talk can really work its magic. And when your little one tries to chat back, give them your full attention – it shows them you’re interested in what they have to say, and they’ll be encouraged to keep going.
It’s important to note that too much screen time isn’t great for babies’ language development. Australian and international guidelines suggest that children under two should ideally have no screen time, except maybe for a bit of video chatting. After all, your baby will find you way more interesting than any screen!
It’s great to use that sing-song baby talk voice, as babies love it. But don’t forget to mix in some regular, adult conversation too. Hearing how words are used in everyday talk is a big part of how your baby learns language.
You might know by now that it’s Little Scholars philosophy that children learn best through play. So with that in mind, we had some ideas about how you can play with your baby and help him or her learn to speak at the same time.
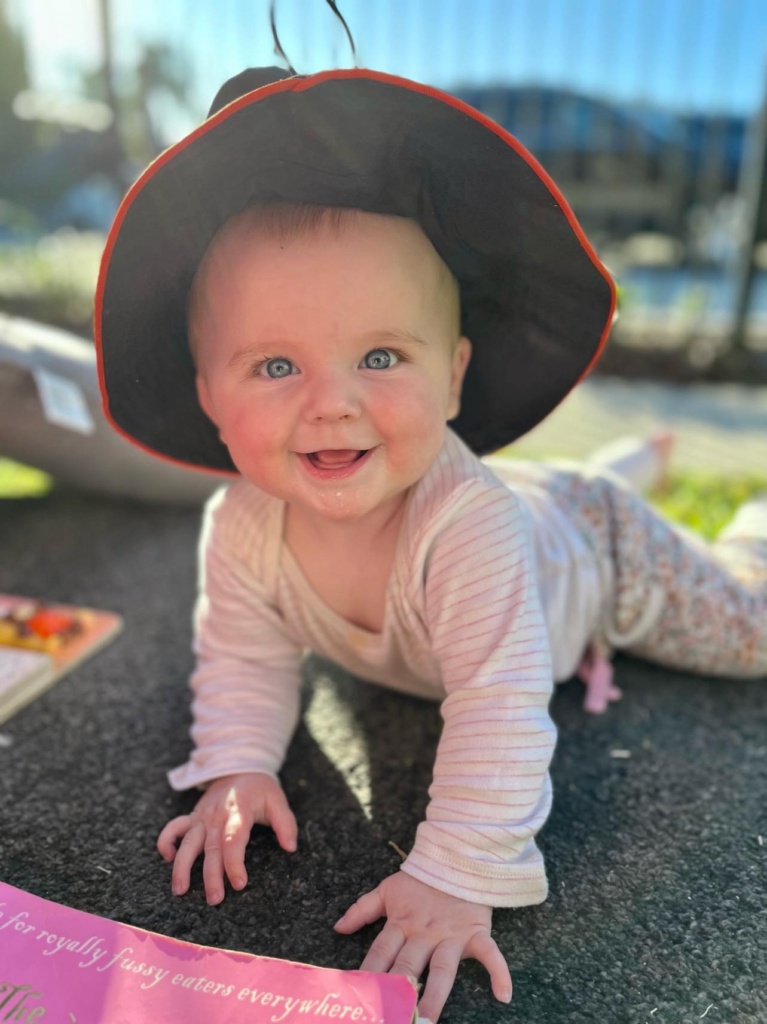

Sasha is a lead educator in one of the toddler studios at Little Scholars Burleigh. She says the Abecedarian Approach is one of her favourite tactics for supporting language development, especially when she’s reading with just one or two children.
“It’s a great way to have back and fourth conversation, for example ‘I can see a horse, can you show me where the horse is?’ or ‘I can see you’re pointing to a monkey, can you find anymore monkeys?’ another one could be ‘I can see you’re point to a dog, what noise does a dog make?’
“It’s not only conversational reading,” Sasha continues. “But also just communicating throughout experiences, if a child is stacking a block on top of another block communicating that action that the child is doing.”
Nikki, the lead educator in the nursery also at our Burleigh campus, says utilising one-on-one periods during routines and rituals, such as nappy changes, washing hands and faces, sunscreen times, are a great time to be talking to the children about what they have been and are doing, ‘we are putting our sunscreen and hats on so we are sun-safe to go outside,’ for example. They also name body parts during the process.
“We always warn the children if we are about to touch their bodies in order to help them, like for nappy changes or sunscreen application, and dictate what is happening to them, so we are verbalising every step,” Nikki says.
“We also talk through the steps at rest times as we place the children in their cots or walk into the cot room, saying ‘we are going to rest our bodies and have some sleep now, I will see you when we wake up and we will do ___’. Basically, we are constantly narrating to the children their every move,” Nikki says.
At our Deception campus, Hayley, lead educator of the toddler studio, does the same thing, but adds a little twist.
“I do a lot of singing, and turning things into songs!” says Hayley. We think that’s a great idea, research shows that singing can help with language development, memory, and even emotional regulation. Singing also has many physical benefits, like improving breathing and posture, and help with early literacy.
“I also think it’s important to be at the child’s level. Talking clearly, and using simple sentences, as well as showing interest when they are speaking to you,” Hayley adds.
Social media can be a great source for parents, so when it comes to baby speech, we’ve got a few we recommend.
Firstly, for all things child-development and early learning, @littlescholarsearlylearning
Then specific for children’s speech development tips, tricks and support, we like these Instagram accounts:
Remember, if you’re worried about your child’s speech development, talk to your GP who can advise or help you with next steps to support your child.
Speech development chart information from Speech Pathology Australia
If you’re a parent of more than one child, or spend time with children of varying ages, you may already see the benefits of those children interacting with each other. In early learning, while we arrange for children of similar ages or development together most of the time, we do make time and space for children to spend time with older and younger children. Why? There’s a lot of research supporting children of various ages and abilities spending time together. We’ll look at a few of these studies and hear from some of our Little Scholars educators who can attest to the advantages of mixing things up!
As an early education provider, we tend to group children together who share similar abilities, who are at similar stages of development or of similar ages. The benefits of this include:
Keeping children together of similar also means they’re stimulated appropriately at each age. Educators can tailor the curriculum to meet the specific developmental needs and milestones common to that age group, making learning more targeted.
As well, being with peers at the same developmental stage allows for more accurate assessment of a child’s progress and needs, aiding in early identification of any learning or developmental challenges, and children of the same age often share similar interests and play preferences, making it easier to form friendships and social bonds.
With a narrower age range, the skill gap between the most and least advanced children in the class is reduced, making group activities more cohesive, and children may feel more at ease and less intimidated when surrounded by peers who are at the same developmental stage, boosting their confidence in social and learning situations.
It also allows educators to be able to use age-appropriate language and teaching methods that resonate with the entire room, making instructions and lessons more effective.
It’s of course true that within ages of studios, for example the nursery, the milestone range can be large – a six month old infant isn’t at the same place a 12-month-old is, and even a 15 month old, but they’re similar enough in their needs that it makes sense to group them together. Our educators plan experiences that focus on movement skills, language development, fine motor development, and strengthening of developmental milestones based on the interests of the babies and research.
For toddlers, who are roughly 18 months to three years old, most are walking by this stage, some of them are learning to speak, sharing with other children and becoming potty trained. For toddlers, the curriculum includes a lot of opportunities for little ones to move their bodies and expel some of that endless energy, but a big focus is on communication and language development, which is why we help your child get to know sounds, words and language, including early literacy and numeracy and social and emotional development.
Then of course, there are our three to five-year-olds, who are further developing their language and literacy skills, fine and gross motor development and more. They are learning to work together in groups as well as individually, all in the build-up to formal schooling.
This is all to say there’s important reasons why our little scholars generally are grouped within similar ages and abilities in their studios. But this does not mean we don’t want them interacting with other children! The opposite, in fact.
The idea to mix aged groups in early learning is of course not a new concept. Here’s two of many theorists of early childhood who supported the idea of bringing children together of mixed age and abilities.
Maria Montessori, the founder of the Montessori method, was a strong advocate for mixed-age classrooms. She believed that older children could serve as role models for younger ones, fostering a sense of community and collaborative learning.
“One of the most important aspects of our education system is the use of the mixed age group which allows all the children to find what is suitable for them, irrespective of their age, and which allows the younger children a graded series of models for imitation, and the older ones the opportunity to reinforce their own knowledge by teaching what they know.”
Now, Montessori classrooms often have children of varying ages working together, which she believed promoted social and emotional development.
Lev Vygotsky, a Russian psychologist, also supported the idea of mixed-age play through his theory of the Zone of Proximal Development (ZPD). According to Vygotsky, children can learn more when they interact with peers who are slightly more advanced than they are. This aligns well with the concept of mixed-age play, where older children can guide younger ones, helping them to reach higher levels of understanding and skill.
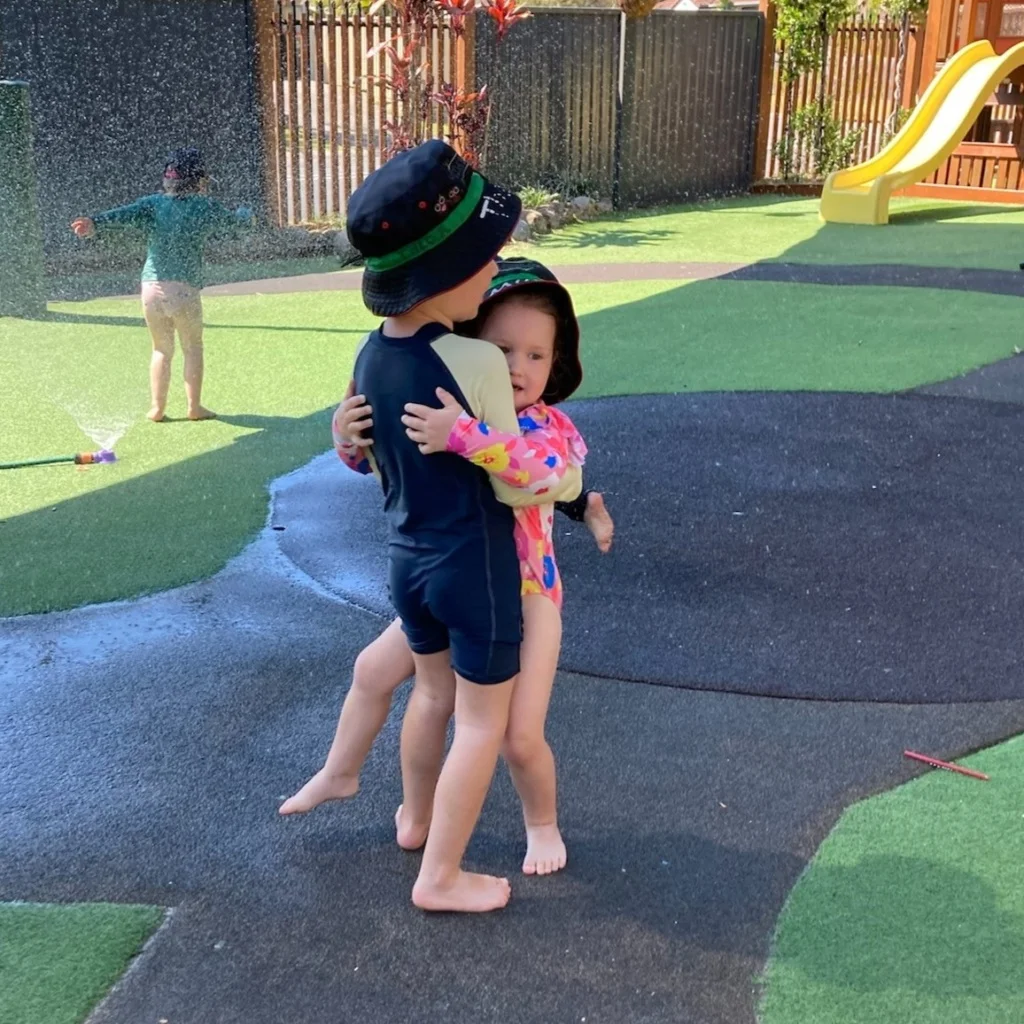

Theo (5) and little sister Mila (3) often get to spend time with each other at our Nerang campus, despite their age difference!
The benefits to having children visit with different age groups are plentiful.
Older children provide leadership and support to younger ones, enhancing skills and confidence for both.
At all of our campuses, there are several sets of siblings. By allowing siblings to interact, it can help younger ones adjust to the care environment.
Even if children don’t have siblings at their campus, mixing with younger children gives them the chance to take on ‘big sibling’ roles.
The benefits also include:
Fosters tolerance and diversity, benefiting children with developmental delays as well.
“I believe that children should have the ability to socialise with children of various age groups,” says Claire, the educational leader at Little Scholars Nerang. “Allowing opportunities for siblings to group together while at the service can assist children to feel a sense of belonging and ease separation anxiety throughout the day.”
For younger children, they can learn from a peer more knowledgeable than themselves, it teaches them problem solving skills and more, says Claire. For the older children, it teaches them nurturing, patience and understanding.
Claire shared a story of one mixed age grouping of two children who weren’t related.

Jacob and Finn are six years apart, share a birthday and have a unique bond at Little Scholars Nerang
“Jacob and Finn are six years apart. Finn began his Little Scholars journey at four months old and took an immediate liking to Jacob aged six at the time. Throughout their friendship, Jacob has assisted Finn to learn how to talk, build and walk. Finn shows great excitement to see Jacob each day by looking for him and can now ask where he is. Finn and Jacob spend time reading and playing together. Jacob uses the abecedarian approach of see, show, say when reading to Finn to build his cognitive skills more specifically language. Each morning and afternoon they spend time together and Finn continues to develop his skill set.
Mixed age grouping for children struggling socially
In 1990, a study in the United States looked at how being in a group with children of different ages could help preschoolers who were having a hard time making friends. The study had 24 children who were either acting out or keeping to themselves. These little ones were put into one of three groups:
The results showed that the children who played with younger, socially skilled children improved the most. They were more likely to make friends and were less likely to act out or keep to themselves.
So, this study tells us that mixing children of different ages can really help those who are struggling to make friends. It can boost their social skills and help them get along better with others.
Complex play in mixed age groups
Another American study found that children in mixed-age classrooms were more likely to engage in complex play modes than children in same-age classrooms.
Over a course of 18 months, there were 47 children who participated. The researchers, from George Mason University, used a variety of methods to collect data, including direct observation, parent questionnaires, and teacher reports.
One of the key findings of the study was that children in mixed-age classrooms interacted more with their same-age peers over time. The researchers suggest that this is because children learn from each other. For example, older children may teach younger children new skills, and younger children may help older children to develop their social skills.
The study also found that older children in mixed-age classrooms became more like younger children, and younger children became more like older children. This is known as bidirectional socialisation. The researchers suggest that bidirectional socialisation may benefit both older and younger children. For example, older children may learn to be more patient and nurturing, and younger children may learn to be more independent and self-reliant.
Overall, the study provides evidence that mixed-age classrooms can have a positive impact on children’s social and behavioral development.
Vocabulary growth in mixed-age groups
A Danish study found that children in mixed-age classrooms had greater gains in vocabulary growth than children in same-age classrooms.
The researchers followed the same group of children over time. The study began when the children were two years and nine months old and ended when they were six years and 11 months old.
The researchers didn’t specify how many trials they conducted, but they did report that the study included 2,743 children. The minimum age difference between children in the same classroom was six months, and the maximum age difference was 24 months. The researchers found classrooms with a maximum age range of 24 months were associated with the greatest gains in vocabulary growth.
To measure children’s vocabulary development, the researchers used a standardised vocabulary test. They gave this test to the children at the beginning of the study and again at the end of the study.
The researchers did not directly observe how the children interacted with each other. However, they did collect data on children’s social interactions through teacher reports and parent questionnaires.
Overall, the study provides evidence that mixed-age classrooms can support children’s language development. However, more research is needed to understand the specific mechanisms through which mixed-age grouping benefits children.
How teachers support mixed age groups
Another study, this time from Sweden in 2022, focused on how preschool teachers implement curricula in different age group settings. The study involved 3,340 children between the ages of two years and nine months and six years and eleven months, from multiple preschools and was based on interviews with teachers.
The study aimed to answer two main questions:
In age-homogeneous groups, teachers felt they could focus on specific age-related goals, whereas in mixed-age groups, the curriculum was more flexible, allowing children to learn at their own pace. The study concluded that both age-homogeneous and mixed-age groups have their own sets of advantages and challenges when it comes to implementing the curriculum.
Researchers focused on the impact of mixed-age groups on children’s development, particularly in vocabulary. The study found that mixed-age groups could be positively linked to individual children’s development, especially in vocabulary.
Advantages of mixed-age groups:
Disadvantages or challenges:
The study suggests that mixed-age groups can be beneficial for children’s development, but they require a specific type of teaching approach.
As you have now read, the benefits of mixed-age play in early learning are plentiful and supported by a wealth of research and educational theories. While it’s common to group children by age or developmental stage, there’s undeniable value in allowing children of different ages to interact. Studies have shown that this kind of grouping can enhance social skills, encourage more complex play, and even boost vocabulary development. Our educators at Little Scholars witness these benefits daily and incorporate mixed-age interactions into our curriculum.
However, it’s not just about mixing ages for the sake of it; it’s about creating a dynamic learning environment that caters to the individual needs of each child. Whether it’s older children mentoring the younger ones or everyone learning to communicate at different levels, the advantages are clear. But it’s not without its challenges; it requires a nuanced approach from educators to ensure that each child’s developmental needs are met. So, while there’s no one-size-fits-all approach to early education, the evidence points towards the value of a mixed-age setting in helping our little scholars grow into well-rounded individuals.
The Case for Mixed-Age Grouping in Early Education (1990) by Lilian G. Katz, Demetra Evangelou, and Jeanette Allison Hartman
The social and behavioral ecology of mixed-age and same-age preschool classrooms: A natural experiment (2002) by Sarah Caverly and Adam Winsler.
Does mixing age groups in early childhood education settings support children’s language development? (2017) by Nina S. Mounts, Jaipaul L. Roopnarine, and Peter B. Smith.
Teaching and learning in age-homogeneous groups versus mixed-age groups in the preschool (2022) by Lena O Magnusson and Kerstin Bäckman
The Little Scholars School of Early Learning recently joined forces with Southern Cross University for an innovative project, looking at how children engage and interact with social robots. NAO is a social robot that has been programmed to interact socially with people and this digital tool has the potential to serve as an educational aide in early learning settings.
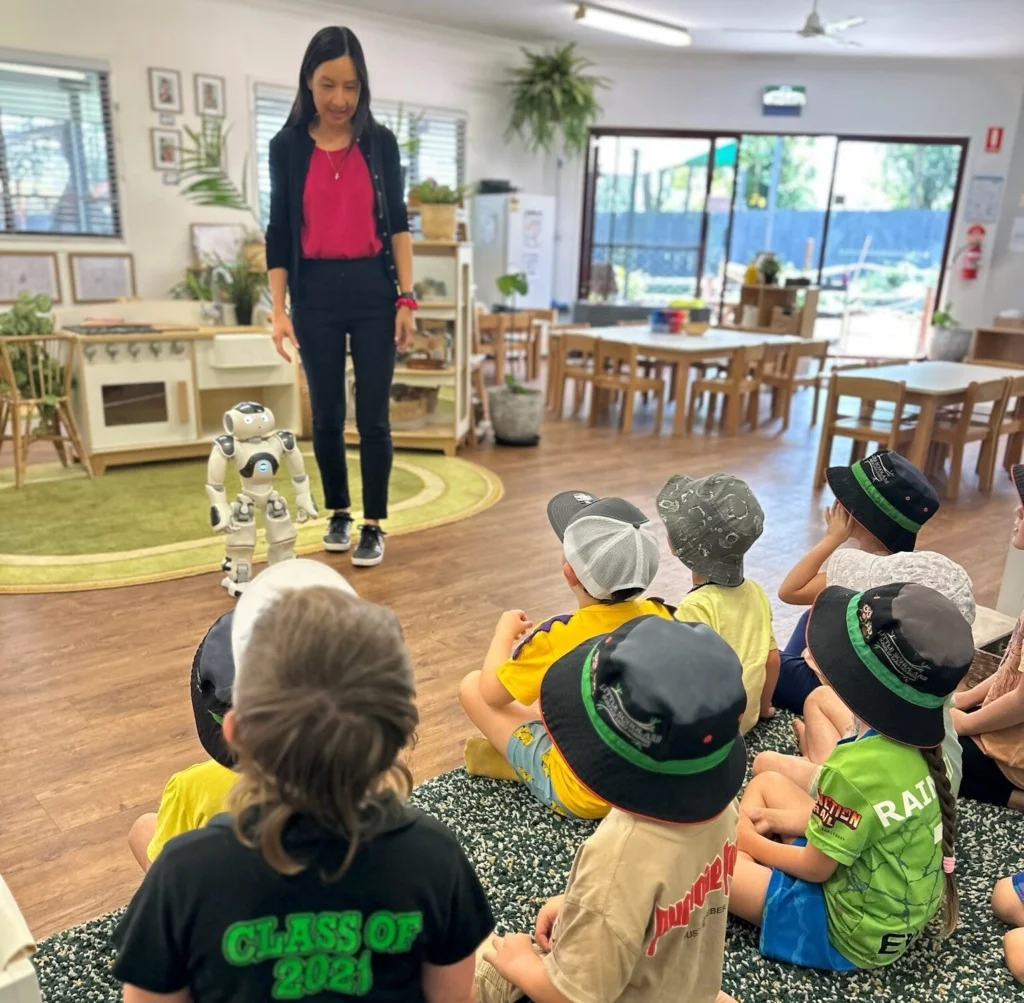

Little Scholars’ Yatala campus was buzzing with excitement as it welcomed Dr Michelle Neumann, Research Assistant Ruby-Jane Barry, and of course, NAO. The visits were part of an educational initiative that captivated the preschool and kindergarten children, as well as educators. The children couldn’t wait to see if Dr. Neumann and NAO had arrived and would dash to the parent lounge to check, educators reported.
The children had the opportunity for one-on-one interactions with NAO, participating in games like ‘Simon Says’, Q&A sessions, and activities focused on literacy.
Dr. Neumann, who leads the project, is an associate professor in early childhood education at Southern Cross University. She believes that this is a frontier that early learning is just starting to venture into.
Interestingly, Dr. Neumann’s journey into early childhood education began after becoming a mum to five children. With an honours degree in science, she decided to pivot her career towards education and early learning. She went back to university, earned her Graduate Diploma in Education, Bachelor of Primary Education, and then completed her PhD focusing on early literacy development. Her dedication has earned her a recent award for research excellence from Southern Cross University, recognising her work in early literacy, digital technologies (tablets, apps, social robots), child development, parent-child interaction.
While NAO has been used to support children’s learning about STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, Maths) and coding, social robots also have the potential to be used to support language, literacy and social learning in the classroom, according to Michelle
“As a physically embodied version of a screen, a social robot may help young children from a range of diverse backgrounds develop their language and social skills,” Michelle said.
“Michelle and Ruby were so approachable and more than willing to let our little scholars meet NAO,” says Raylene, lead educator in the senior kindergarten room. “I was fascinated with NAO’s abilities, and the potential social robots could have in a classroom setting. As a lead educator, the benefits of having an additional learning assistant was something I was happy to advocate for, so I was quick to start drumming up more families to participate in the visits.”
Raylene said she had a lot of conversations with children preparing them for NAO’s visit, even conversations that maybe one day, the children might have robot friends to help their teachers in the classrooms.
“This was super exciting for the children. I did have to remind them and to the families that it wasn’t happening straight away, but the concept was well received. Families enjoyed the debates of whether it would take jobs from educators, and I enjoyed discussing this with them. By day two, Michelle and Ruby were needing to organise additional days to attend the service due to the influx of families wanting to participate,” Raylene said.
Raylene said on the first day, it was evident that although the children were excited, there were also plenty of nerves. Most of the children participated well, with a small handful quite shy, she said. As the program continued, the children got used to seeing Michelle, Ruby and NAO in the parent lounge, those children who were a little shy to begin with looked eager to have another turn.
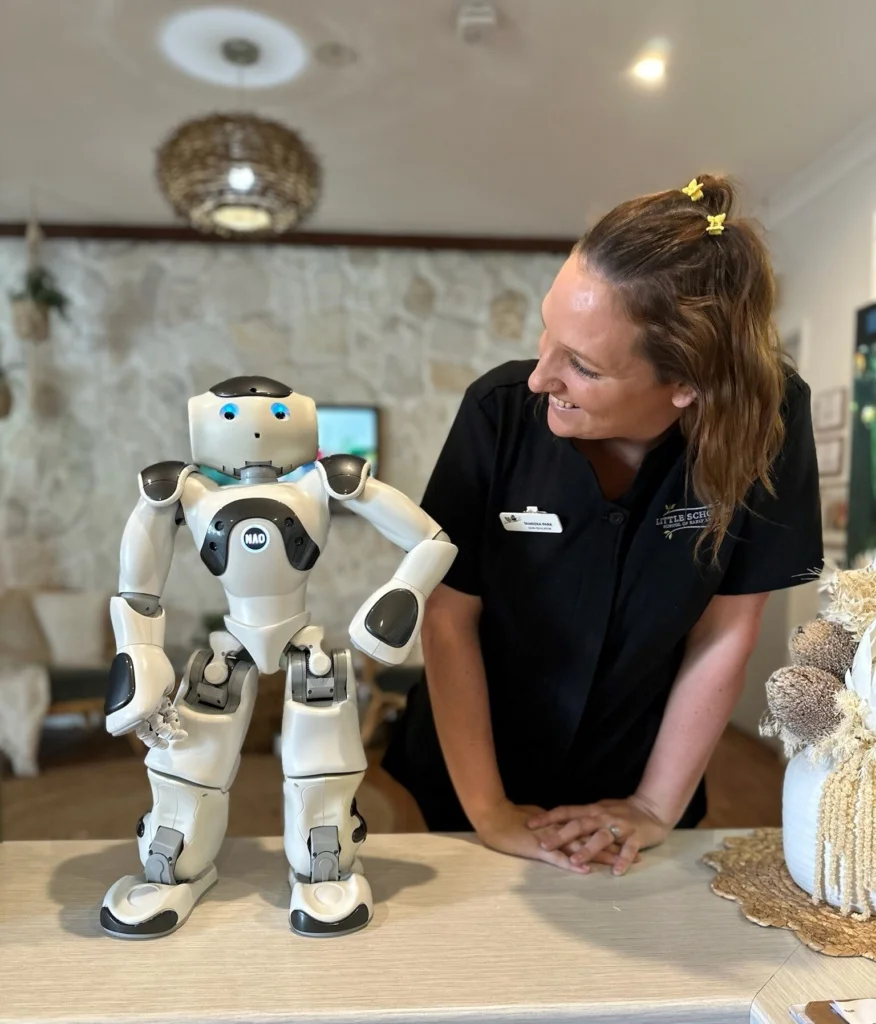

“This was obvious in my own son Tannen. Tannen was one of the few who participated on day one. The whole lead up was a confident ‘I’m having a robot friend’ until he got his robot friend,” Raylene said. “After his turn he told me he didn’t like it a lot because it was scary, however as the days went on, and more friends started to participate, and NAO became a familiar face, all of a sudden he was eager to come to the door to see if they were there yet, and talk to other children on the way in to see if they were going to go and play games with NAO that day. This is the way it unfolded for several children,” Raylene said.
After a few one-on-one visits to introduce NAO to children, Michelle made a final visit to introduce more campus children to NAO and play some games.
“You could see the comfort of the children who were already familiar with NAO, and it acted like a scaffold for the children who hadn’t had the chance yet to interact with him. Comments from children like ‘Oh, that’s just NAO’ and ‘I already played this game and it’s really fun’ to encourage peers along were incredible to hear because it was listening to four- to five-year-olds comforting each other and being confident with the experiences they had just had,” Raylene said.
Michelle said one day she’d love to introduce a full program which sees social robots in more early learning classrooms. But, she says, these are still relatively early days. Social robots are a work in progress, and she acknowledges they’re limited in what they can currently do. She’d love to also work with children who would benefit from additional language and literacy support. For that to work, NAO’s voice recognition needs development as it would need to have the ability to understand a spectrum of language milestones, she said.
“It would take a lot of time, guidance and professional development for educators… and a lot of support to be able to use the social robot in its current form,” she said. “But they’re working on AI generated social robots and these innovative opportunities may make using social robots more usable in the classroom.”
And, the robots are not cheap. NAO can cost up to $20,000 AUD, which she acknowledges would be financially prohibitive to many early learning settings. Michelle says her hope is that more research to can be done to better understand the role that social robots could play in supporting young children’s early learning experiences. With emerging advances in robotics, it may be possible that the production costs of these devices could one day become a more affordable educational tool.
The collaboration between Little Scholars and Southern Cross University has opened up new avenues for early learning, showcasing the potential of integrating social robots like NAO into educational settings. The overwhelmingly positive response from both children and educators alike underscores the limitless possibilities this technology could offer. As we look to the future, the hope is that advancements in AI and robotics will make these educational tools more accessible and tailored to the unique needs of early learners. This pioneering initiative serves as a testament to the boundless curiosity and adaptability of children, and the commitment of educators like Michelle and Raylene to push the boundaries of what’s possible in early education.
Jae Fraser, founder of Little Scholars, wholeheartedly supports the NAO project with Little Scholars.
“This is such an exciting project for our little scholars to engage in,” he says. “Introducing social robots to Little Scholars, isn’t just a leap in technology; it’s a giant step in nurturing young minds.
“We look forward to where this will go, and how we can use resources like this to continue the learning journey for Little Scholars.”
Additional information
The potential of social robots in early learning includes:
Potential barriers and obstacles for social robots in early learning:
At Little Scholars School of Early Learning, we’re dedicated to shaping bright futures and instilling a lifelong passion for learning. With our strategically located childcare centres in Brisbane and the Gold Coast, we provide tailored educational experiences designed to foster your child’s holistic development.
Let us hold your hand and help looking for a child care centre. Leave your details with us and we’ll be in contact to arrange a time for a ‘Campus Tour’ and we will answer any questions you might have!
"*" indicates required fields
Let us hold your hand and help looking for a child care centre. Leave your details with us and we’ll be in contact to arrange a time for a ‘Campus Tour’ and we will answer any questions you might have!
"*" indicates required fields